
Reimagining Enterprise Decision-Making With Artificial Intelligence
Add Your Heading Text Here

Artificial Intelligence will deliver revolutionary impact on how enterprises make decisions today. In the last few years alone, we have rapidly moved beyond heuristics-based decision-making to analytics-driven decision-support. In the VUCA phase, businesses globally are now pivoting to an AI-led, algorithm-augmented style of decision-making. With huge computing power and ever-increasing data storage and analytics prowess, we are entering a new paradigm, a probable and interesting scenario wherein, Artificial Intelligence will play a huge role in augmenting human intelligence and enabling decision-making with complete autonomy. The big hope is that this new paradigm will not only reduce human biases and errors that are common with heuristic decisions, but also reduce the time involved in making these critical decisions.
Here, I’ll attempt to focus on how we moved from simpler data driven decision-support to AI-powered decisions. The evolution of this technology has been breathtaking to behold and just might provide clues as to what we can expect in the future. Further, I’ll cover a few critical aspects that need to be inculcated by organizations on the AI transformation journey, and provide a few insightful cues that will make this journey exciting and fruitful.
Transformation of Decision-Making: From Analytics to AI
First, let us look at how we got here. Some truly pathbreaking events happened along the way while we were trying to make more accurate business decisions, leading us to reimagine how decisions will be made in the enterprise.
Organizations are Becoming Math Houses
With data deluge and digital detonation, combined with the appreciation of the fact that robust analytical capabilities lead to more informed decisions, we are witnessing AI savvy organizations rapidly maturing into ‘math houses.’ Data science – the ability to extract meaningful insights out of data has become de rigueur. Why? Because we now know that data, when seen in isolation, is inherently dumb. It is the ability to process this data and identify patterns and anomalies – using sophisticated algorithms and ensemble techniques – that makes all the difference. These self-intuitive algorithms are where real value resides – as they define the intelligence required to uncover insights and make smart recommendations. Organizations today are evolving into algorithm factories. There is a real understanding today that by enabling continuous advancement in mathematical algorithms, we can deliver consistent decisions based on prescribed as well as evolving business rules.
It is now an established reality that companies with robust mathematical capabilities possess a huge advantage over those that don’t. Indeed, it’s this math-house orientation that separates companies like Amazon and Google from the ones they leave in their wake, with their ability to understand their customers better, identify anomalies and recognize key patterns.
AI: From Predictive to Prescriptive
We saw a similar evolution in the age of analytics – wherein the science and value veered from descriptive analytics, providing diagnostics of past events to prescriptive analytics, helping see and shape the future. We are seeing a similar evolution in how AI gets leveraged in the enterprise and where its maximum value lies.
In early implementations, it was common to see AI as just a tool to predict and forecast future conditions, while accounting for the dynamism seen in the external environment. Today, AI-enabled decision-making is more prescriptive, with AI providing enterprises not just a look into the future, but also key diagnostics and suggestions on potential decision options and their payoffs. Such evolved applications of AI can help businesses make decisions that can potentially exploit more business opportunities, while averting potential threats much earlier.
Mr. Algorithm to Drive Decision Making
The culmination of this AI-era advancement would be the introduction of smart algorithms in every walk of life and business. Algorithms will become further mainstream leading to what will be the most sweeping business change since the industrial revolution. Organizations – those that already aren’t – will start developing a suite of algorithmic IP’s that will de-bias most enterprise decisions.
If Mr. Algorithm is going to drive most enterprise decisions of tomorrow, we need to create some checks and balances to ensure that it does not go awry. It is more critical today than ever before that the algorithmic suite developed by enterprises has a strong grounding in ethics and can handle situations appropriately for which explicit training may not have been provided.
How to Enable this AI Era of Change
Ushering into an AI-centric era of decision-making will require organizational transformation from business, cultural and technical standpoints. The following facets will be the enablers of this change:
Developing an Engineering Mindset
Instrumenting AI in the enterprise requires a combination of data scientists and computer scientists. As AI matures in the enterprise, the users, use cases and data will increase exponentially. To deliver impactful AI applications, scale and extensibility is critically important. This is where having an engineering mindset comes in. Imbibing an engineering mindset will help standardize the use of these applications while ensuring that they are scalable and extensible.
Learning, Unlearning, Relearning
The other critical aspect to a culture where AI can thrive is creating an environment supporting continuous unlearning and relearning. AI can succeed if the people developing and operating it are rewarded for continuous experimentation and exploration. And just like AI, people should be encouraged to incorporate feedback loops and learn continuously. As technology matures it’s important that the existing workforce keeps up. For one, it’s critical that the knowledge of algorithm theory, applied math alongside training on AI library and developer tools, is imparted into the workforce – and is continuously updated to reflect new breakthroughs in this space.
Embedding Design-Thinking and Behavioral Science at the Center of this Transformation
Finally, given the nature of AI applications, it’s critical that they are consumed voraciously. User input very often activates the learning cycles of artificial intelligence applications. To ensure high usage of these applications, it’s very important that we put the user at the center while designing these applications. This is where the application of behavioral sciences and human-centered design will deliver impact. By imparting empathy in these applications for the user, we will be able to design better and more useful AI applications.
As we augment decision-making with algorithmic, AI-centered systems and platforms – the big expectation is that they will bring untold efficiencies in terms of cost, alongside improvement in the speed and quality with which decisions get made. It’s time to reimagine and deliver on enterprise decision-making that is increasingly shaped through artificial intelligence. These aspects – how the AI is progressing and how to exploit its potential are of paramount importance to keep in mind for an AI transformation.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS
How AI is Challenging Management Theories and Disrupting Conventional Strategic Planning Processes
Add Your Heading Text Here

When it comes to AI, businesses think ambitiously. Nearly 85% of executives believe AI will allow their company to obtain or sustain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Contrastingly, just one in five companies have incorporated AI into their organization and less than 39% of companies have an AI strategy.
Exactly why is AI so disruptive to traditional business models and traditional notions of industry competition? A useful way to analyse the situation is by looking at Porter’s model of the five forces of industry competition and exploring how artificial intelligence is impacting each of the various forces.
According to Michael E. Porter, in one of his landmark books, titled Competitive Strategy, “In any industry, whether it is domestic or international or produces a product or a service, the rules of competition are embodied in five competitive forces: the entry of new competitors, the threat of substitutes, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the rivalry among the existing competitors.”
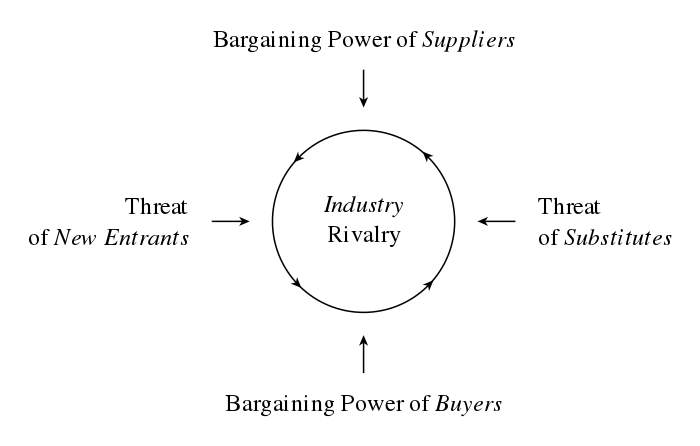
Figure 1: Porter’s Five Forces
Let’s look at each of these five forces and examine the role and impact of AI:
The entry of new competitors
There’s no doubt that AI is changing the nature of competition. Today, it’s not just traditional industry competitors you need to worry about, but new entrants from outside your industry, equipped with new AI based business models and value propositions.
This is often tech giants and startups that have envisioned and built a new business model from the ground up, powered by a new platform ecosystem for AI. They’re leveraging the familiar social, mobile, analytics and cloud technologies, but are often adding in personas and context, intelligent automation, chatbots and the Internet of Things, to further enhance the value proposition of their platform.
Why can new entrants move in so easily? Digital business changes the rules by lowering the traditional barriers to entry. A digitally based business model requires far less capital and can bring large economies of scale for example. Read more about how AI Startups are creating disruptive competition here.
The threat of substitutes
The threat of substitutes is high in many industries since switching costs are low and buyer propensity to substitute is high. For example, In the taxi services, customers can easily switch from traditional models to the new digital app based taxi services, employing AI routines to create differential pricing and intelligent route mapping to increase margin as well as decrease price for the customers. Propensity to switch from the traditional model is high due to consumer wait times for taxis, lack of visibility into taxi location and so on.
In case of BPO industry, the advent of AI has been extremely disruptive, with their clients completely substituting their services with building in-house automation offerings and circumventing their need, sometimes completely. Read more in detail about the disruption of BPO/BPM by AI here.
The bargaining power of buyers
Perhaps the strongest of the five forces impacting industry competition is the bargaining power of buyers since the biggest driver of AI and digital business comes from the needs and expectations of consumers and customers themselves.
This bargaining power lays out a new set of expectations for the AI and digital customer experience and necessitates continual corporate innovation across business models, processes, operations, products and services.
For example, the most used instances of chatbots are through customer support, and now they are heading in the direction of changing the retail sector altogether. The expectations of the Millennials are directing the course of this new technology. This is why chatbots have the burden to exceed the expectations in the retail sector.
Also, in another example, in the customer facing marketing aspect, AI is causing circular rise in customer expectations as rise of expectations, mostly from millennials, has forced the companies to adopt an AI solution to the problem, which further has emboldened their expectations. Amazon, the company that wants to eat everyone’s lunch, is already driving a third of its business from a AI-powered function: its recommended purchases. Read more about how AI is accentuating customer experience to address rising expectations Here.
The bargaining power of suppliers
Suppliers can accelerate or slow down the adoption of a AI based business model based upon how it impacts their own situation. Those pursuing AI models themselves, such as the use of APIs to streamline their ability to form new partnerships and manage existing ones, may help accelerate your own model.
Those who are suppliers to the traditional models, and who question or are still determining their new role in the digital equivalent, may use their bargaining power to slow down or dispute the validity or legality of the new model.
Good examples are the legal and business issues surfacing around the digital-sharing economy (i.e. ride-sharing, room-sharing etc.) where suppliers and other constituents work to ensure the AI based business model and process innovations (like route optimization, or deep customer behaviour analysis using private data) still adhere to established rules, regulations, privacy, security and safety. This is a positive and needed development since, coupled with bargaining power of buyers, it can help to keep new models “honest” in terms of how they operate.
The rivalry among the existing competitors
A lot of organisations are in exploratory stages as they realise that their strategy and customer engagement needs to get smarter. The combination of optimism and fear that clients today have shows that for them it is a competitive necessity to adopt AI and digital technologies.
In 20 years, probably every job will be touched by AI. The technology is growing universally. WhatsApp and Facebook — everything is driven by AI. And what this means is that on the job front, there may be blood. Once AI, ML, and virtual and augmented reality go mainstream, these technologies will prove to be a huge job creator.
But currently, the most competitive space in AI adoption is in the implementation of chatbots across industries and functions. While we might see chatbots starting to appear through the likes of Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp platforms in the coming 12 months, and will be dedicating teams of engineers to train the platforms, rather than relying on the general public. Read more about the competitive atmosphere and underlying need to better customer experience using chatbot here.
How AI will transform Strategic Planning Process
How can managers — from the front lines to the C-suite — thrive in the age of AI? In many ways, the lack of understanding when it comes to AI is due to the variety of ways AI can be implemented as a part of strategic planning for a business. Different industries, or even different companies within the same industry, may use AI in different ways. Ping An, which employs 110 data scientists, has launched about 30 CEO-sponsored AI initiatives that support, in part, its vision – that technology will be the key driver to deliver top-line growth for the company in the years to come. Yet in sharp contrast, elsewhere in the insurance industry, other large companies’ AI initiatives are limited to experimenting with chatbots. Obviously, integrating AI is not going to be simple. There will be a massive learning curve for organizations before they’re able to start implementing AI effectively. But the core shift in strategic planning will happen in the following ways:
AI will take over almost all Administrative Tasks
According to an HBR report, managers across all levels spend more than half of their time on administrative coordination and control tasks. (For instance, a typical store manager or a lead nurse at a nursing home must constantly juggle shift schedules because of staff members’ illnesses, vacations, or sudden departures.) These are the very responsibilities that the same managers expect to see AI affecting the most. And they are correct: AI will automate many of these tasks.

Figure 2: Source – HBR (How Artificial Intelligence Will Redefine Management)
For example, in case of report writing The Associated Press expanded its quarterly earnings reporting from approximately 300 stories to 4,400 with the help of AI-powered software robots. In doing so, technology freed up journalists to conduct more investigative and interpretive reporting.
Strategy Managers will focus more on Judgement-oriented Creative Thinking Work
The human factor, which AI still cannot permeate – the application of experience, expertise and a capacity to improvise, to critical business decisions and practices – need to be focused on by strategy managers. Many decisions require insight beyond what artificial intelligence can squeeze from data alone. Managers use their knowledge of organizational history and culture, as well as empathy and ethical reflection. Managers we surveyed have a sense of a shift in this direction and identify the creative thinking skills and experimentation, data analysis and interpretation, and strategy development as three of the four top new skills that will be required to succeed in the future. And since the potential of machine learning is the ability to help make decisions, the AI technology would be better placed as an assisting hand than administrative mind.
Think of AI not as Machines, but Colleagues
Managers who view AI as a kind of colleague will recognize that there’s no need to “race against a machine.” While human judgment is unlikely to be automated, intelligent machines can add enormously to this type of work, assisting in decision support and data-driven simulations as well as search and discovery activities. In fact, 78% of the surveyed managers believe that they will trust the advice of intelligent systems in making business decisions in the future.
Not only will AI augment managers’ work, but it will also enable managers to interact with intelligent machines in collegial ways, through conversation or other intuitive interfaces.
For example, Kensho Technologies, a provider of next-generation investment analytics, allows investment managers to ask investment-related questions in plain English, such as, “What sectors and industries perform best three months before and after a rate hike?” and get answers within minutes.
Design Thinking needs to be adopted both ways – Managers & AI
While managers’ own creative abilities are vital, perhaps even more important is their ability to harness others’ creativity. Manager-designers bring together diverse ideas into integrated, workable, and appealing solutions. Creative thinking and experimentation is a key skill area that managers need to learn to stay successful as AI increasingly takes over administrative work. ‘Collaborative Creativity’ is the operating word here.
But this doesn’t mean that design thinking necessarily need to become a forte exclusive to managers. Even though AI engines may not have reached radical thinking and improvisation as humans, AI algorithms should be viewed as cognitive tools capable of augmenting human capabilities and integrated into systems designed to go with the grain of human—and organizational—psychology. This calls for Divergence from More Powerful Intelligence To More Creative Intelligence in AI.
To make design thinking meaningful for consumers, companies can benefit from carefully selecting use cases and the information they feed into AI technologies. In determining which available data is likely to generate desired results, enterprises can start by focusing on their individual problems and business cases, create cognitive centres of excellence, adopt common platforms to digest and analyze data, enforce strong data governance practices, and crowdsource ideas from employees and customers alike. Read more about Design Thinking in AI here.
Create New Business Processes manifested from Augmented Working Strategy
Simply put, my recommendation is to adopt AI in order to automate administration and to augment but not replace human judgment. If the current shortage of analytical talent is any indication, organizations can ill afford to wait and see whether their managers are equipped to work alongside AI. This calls for change in business processes, and the way they are implemented itself. To navigate in an uncertain future, managers must explore early, and experiment with AI and apply their insights to the next cycle of experiments.
AI augmentation will drive the adoption of new key performance indicators. AI will bring new criteria for success: collaboration capabilities, information sharing, experimentation, learning and decision-making effectiveness, and the ability to reach beyond the organization for insights.
Accordingly, organizations need to develop training and recruitment strategies for creativity, collaboration, empathy, and judgment skills. Leaders should develop a diverse workforce and team of managers that balance experience with creative and social intelligence — each side complementing the other to support sound collective judgment.
Final Word
While oncoming AI disruptions in Management Principles and Strategic Planning space won’t arrive all at once, the pace of development is faster and the implications more far-reaching than most executives and managers realize. Those managers capable of assessing what the workforce of the future will look like can prepare themselves for the arrival of AI.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Design Thinking | Behavioural Sciences: Strategic Elements to Building a Successful AI Enterprise
Add Your Heading Text Here

Today’s artificial intelligence (AI) revolution has been made possible by the algorithm revolution. The machine learning algorithms researchers have been developing for decades, when cleverly applied to today’s web-scale data sets, can yield surprisingly good forms of intelligence. For instance, the United States Postal Service has long used neural network models to automatically read handwritten zip code digits. Today’s deep learning neural networks can be trained on millions of electronic photographs to identify faces, and similar algorithms may increasingly be used to navigate automobiles and identify tumors in X-rays. The IBM Watson information retrieval system could triumph on the game show “Jeopardy!” partly because most human knowledge is now stored electronically.
But current AI technologies are a collection of big data-driven point solutions, and algorithms are reliable only to the extent that the data used to train them is complete and appropriate. One-off or unforeseen events that humans can navigate using common sense can lead algorithms to yield nonsensical outputs.
Design thinking is defined as human-centric design that builds upon the deep understanding of our users (e.g., their tendencies, propensities, inclinations, behaviours) to generate ideas, build prototypes, share what you’ve made, embrace the art of failure (i.e., fail fast but learn faster) and eventually put your innovative solution out into the world. And fortunately for us humans (who really excel at human-centric things), there is a tight correlation between the design thinking and artificial intelligence.
Artificial intelligence technologies could reshape economies and societies, but more powerful algorithms do not automatically yield improved business or societal outcomes. Human-centered design thinking can help organizations get the most out of cognitive technologies.
Divergence from More Powerful Intelligence To More Creative Intelligence
While algorithms can automate many routine tasks, the narrow nature of data-driven AI implies that many other tasks will require human involvement. In such cases, algorithms should be viewed as cognitive tools capable of augmenting human capabilities and integrated into systems designed to go with the grain of human—and organizational—psychology. We don’t want to ascribe to AI algorithms more intelligence than is really there. They may be smarter than humans at certain tasks, but more generally we need to make sure algorithms are designed to help us, not do an end run around our common sense.
Design Thinking at Enterprise Premise
Although cognitive design thinking is in its early stages in many enterprises, the implications are evident. Eschewing versus embracing design thinking can mean the difference between failure and success. For example, a legacy company that believes photography hinges on printing photographs could falter compared to an internet startup that realizes many customers would prefer to share images online without making prints, and embraces technology that learns faces and automatically generates albums to enhance their experience.
To make design thinking meaningful for consumers, companies can benefit from carefully selecting use cases and the information they feed into AI technologies. In determining which available data is likely to generate desired results, enterprises can start by focusing on their individual problems and business cases, create cognitive centres of excellence, adopt common platforms to digest and analyze data, enforce strong data governance practices, and crowdsource ideas from employees and customers alike.
In assessing what constitutes proper algorithmic design, organizations may confront ethical quandaries that expose them to potential risk. Unintended algorithmic bias can lead to exclusionary and even discriminatory practices. For example, facial recognition software trained on insufficiently diverse data sets may be largely incapable of recognizing individuals with different skin tones. This could cause problems in predictive policing, and even lead to misidentification of crime suspects. If the training data sets aren’t really that diverse, any face that deviates too much from the established norm will be harder to detect. Accordingly, across many fields, we can start thinking about how we create more inclusive code and employ inclusive coding practices.
CXO Strategy for Cognitive Design Thinking
CIOs can introduce cognitive design thinking to their organizations by first determining how it can address problems that conventional technologies alone cannot solve. The technology works with the right use cases, data, and people, but demonstrating value is not always simple. However, once CIOs have proof points that show the value of cognitive design thinking, they can scale them up over time.
CIOs benefit from working with business stakeholders to identify sources of value. It is also important to involve end users in the design and conception of algorithms used to automate or augment cognitive tasks. Make sure people understand the premise of the model so they can pragmatically balance algorithm results with other information.
Enterprise Behavioral Science – From Insights to Influencing Business Decisions
Every January, how many people do you know say that they want to resolve to save more, spend less, eat better, or exercise more? These admirable goals are often proclaimed with the best of intentions, but are rarely achieved. If people were purely logical, we would all be the healthiest versions of ourselves.
However, the truth is that humans are not 100% rational; we are emotional creatures that are not always predictable. Behavioral economics evolved from this recognition of human irrationality. Behavioral economics is a method of economic analysis that applies psychological insights into human behavior to explain economic decision-making.
Decision making is one of the central activities of business – hundreds of billions of decisions are made everyday. Decision making sits at the heart of innovation, growth, and profitability, and is foundational to competitiveness. Despite this degree of importance, decision making is poorly understood, and badly supported by tools. A study by Bain & Company found that decision effectiveness is 95% correlated with companies’ financial performance.
Enterprise Behavioral Science is not only about understanding potential outcomes, but to completely change outcomes, and more specifically, change the way in which people behave. Behavioral Science tells us that to make a fundamental change in behavior that will affect the long-term outcome of a process, we must insert an inflection point.
As an example, you are a sales rep and two years ago your revenue was $1 million. Last year it was $1.1 million, and this year you expect $1.2 million in sales. The trend is clear, and your growth has been linear and predictable. However, there is a change in company leadership and your management has increased your quota to $2 million for next year. What is going to motivate you to almost double your revenues? The difference between expectations ($2 million) and reality ($1.2 million) is often referred to as the “behavioral gap” . When the behavioral gap is significant, an inflection point is needed to close that gap. The right incentive can initiate an inflection point and influence a change in behavior. Perhaps that incentive is an added bonus, President’s Club eligibility, a promotion, etc.
Cognitive Design Thinking – The New Indispensable Reskilling Avenue
Artificial intelligence, machine learning, big data analytics and mobile and software development will be the top technology areas where the need for re-skilling will be the highest. India will need 700 million skilled workforce by 2022 to meet the demands of a growing economy. Hence, while there is a high probability that machine learning and artificial intelligence will play an important role in whatever job you hold in the future, there is one way to “future-proof” your career…embrace the power of design thinking.
In fact, integrating design thinking and artificial intelligence can give you “super powers” that future-proof whatever career you decide to pursue. To meld these two disciplines together, one must:
- Understand where and how artificial intelligence and behavioural science can impact your business initiatives. While you won’t need to write machine learning algorithms, business leaders do need to learn how to “Think like a data scientist” in order understand how AI can optimize key operational processes, reduce security and regulatory risks, uncover new monetization opportunities.
- Understand how design thinking techniques, concepts and tools can create a more compelling and emphatic user experience with a “delightful” user engagement through superior insights into your customers’ usage objectives, operating environment and impediments to success.
Design thinking is a mindset. IT firms are trying to move up the curve. Higher-end services that companies can charge more is to provide value and for that you need to know that end-customers needs. For example, to provide value services to banking customers is to find out what the bank’s customer needs are in that country the banking client is based. Latent needs come from a design thinking philosophy where you observe customer data, patterns and provide a solution that the customer does not know. Therefore, Companies will hire design thinkers as they can predict what the consumer does not know and hence charge for the product/service from their clients. Idea in design thinking is to provide agile product creation or solutions.
Without Design Thinking & Behavioural Science, AI Will be Only an Incremental Value
Though organizations understand the opportunity that big data presents, many struggles to find a way to unlock its value and use it in tandem with design thinking – making “big data a colossal waste of time & money.” Only by combining quantitative insights gathered using AI, machine/deep learning, and qualitative research through behavioural science, and finally design thinking to uncover hidden patterns and leveraging it to understand what the customer would want, will we be able to paint a complete picture of the problem at hand, and help drive towards a solution that would create value for all stakeholders.

