
Lock in winning AI deals : Strategic recommendations for enterprises & GCCs
Add Your Heading Text Here

Artificial Intelligence is unleashing exciting growth opportunities for the enterprises & GCCs , at the same time , they also present challenges and complexities when sourcing, negotiating and enabling the AI deals . The hype surrounding this rapidly evolving space can make it seem as if AI providers hold the most power at the negotiation table. After all, the market is ripe with narratives from analysts stating that enterprises and GCCs failing to embrace and implement AI swiftly run the risk of losing their competitiveness. With pragmatic approach and acknowledgement of concerns and potential risks, it is possible to negotiate mutually beneficial contracts that are flexible, agile and most importantly, scalable. The following strategic choices will help you lock in winning AI deals :
Understand AI readiness & roadmap and use cases
It can be difficult to predict exactly where and how AI can be used in the future as it is constantly being developed, but creating a readiness roadmap and identifying your reckoner of potential use cases is a must. Enterprise and GCC readiness and roadmap will help guide your sourcing efforts for enterprises and GCCs , so you can find the provider best suited to your needs and able to scale with your business use cases. You must also clearly frame your targeted objectives both in your discussions with vendors as well as in the contract. This includes not only a stated performance objective for the AI , but also a definition of what would constitute failure and the legal consequences thereof.
Understand your service provider’s roadmap and ability to provide AI evolution to steady state
Once you begin discussions with AI vendors & providers, be sure to ask questions about how evolved their capabilities and offerings are and the complexity of data sets that were used to train their system along with the implementation use cases . These discussions can uncover potential business and security risks and help shape the questions the procurement and legal teams should address in the sourcing process. Understanding the service provider’s roadmap will also help you decide whether they will be able to grow and scale with you. Gaining insight into the service provider’s growth plans can uncover how they will benefit from your business and where they stand against their competitors. The cutthroat competition among AI rivals means that early adopter enterprises and GCCs that want to pilot or deploy AI@scale will see more capabilities available at ever-lower prices over time. Always mote that the AI service providers are benefiting significantly from the use cases you bring forward for trial as well as the vast amounts of data being processed in their platforms. These points should be leveraged to negotiate a better deal.
Identify business risk cycles & inherent bias
As with any implementation, it is important to assess the various risks involved. As technologies become increasingly interconnected, entry points for potential data breaches and risk of potential compliance claims from indirect use also increase. What security measures are in place to protect your data and prevent breaches? How will indirect use be measured and enforced from a compliance standpoint? Another risk AI is subject to is unintentional bias from developers and the data being used to train the technology. Unlike traditional systems built on specific logic rules, AI systems deal with statistical truths rather than literal truths. This can make it extremely difficult to prove with complete certainty that the system will work in all cases as expected.
Develop a sourcing and negotiation plan
Using what you gained in the first three steps, develop a sourcing and negotiation plan that focuses on transparency and clearly defined accountability. You should seek to build an agreement that aligns both your enterprise’s and service provider’s roadmaps and addresses data ownership and overall business and security related risks. For the development of AI , the transparency of the algorithm used for AI purposes is essential so that unintended bias can be addressed. Moreover, it is appropriate that these systems are subjected to extensive testing based on appropriate data sets as such systems need to be “trained” to gain equivalence to human decision making. Gaining upfront and ongoing visibility into how the systems will be trained and tested will help you hold the AI provider accountable for potential mishaps resulting from their own erroneous data and help ensure the technology is working as planned.
Develop a deep understanding of your data, IP, commercial aspects
Another major issue with AI is the intellectual property of the data integrated and generated by an AI product. For an artificial intelligence system to become effective, enterprises would likely have to supply an enormous quantity of data and invest considerable human and financial resources to guide its learning. Does the service provider of the artificial intelligence system acquire any rights to such data? Can it use what its artificial intelligence system learned in one company’s use case to benefit its other customers? In extreme cases, this could mean that the experience acquired by a system in one company could benefit its competitors. If AI is powering your business and product, or if you start to sell a product using AI insights, what commercial protections should you have in place?
In the end , do realize the enormous value of your data, participate in AI readiness, maturity workshops and immersion sessions and identification of new and practical AI use cases. All of this is hugely beneficial to the service provider’s success as well and will enable you to strategically source and win the right AI deal.
(AIQRATE advisory & consulting is a bespoke global AI advisory & consulting firm and provides strategic advisory services to boards, CXOs, senior leaders to curate , design building blocks of AI strategy , embed AI@scale interventions & create AI powered enterprises . Visit www.aiqrate.ai , reach out to us at consult@aiqrate.ai )
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS
AI-Driven Disruption And Transformation: New Business Segments To Novel Market Opportunities
Add Your Heading Text Here

There’s little doubt that Artificial Intelligence (AI) is driving the decisive strategic elements in multiple industries, and algorithms are sitting at the core of every business model and in the enterprise DNA. Conventional wisdom, based on no small amount of research, holds that the rise of AI will usher radical, disruptive changes in the incumbent industries and sectors in the next five to 10 years.
Additionally, it’s never been a better time to launch an AI venture. Investments in AI-focused ventures have grown 1800% in just six years. The rationale behind these numbers comes, in part, from the fact that enterprises expect AI to enable them to move into new business segments, or to maintain a competitive edge in their industry.
Strategists believe this won’t come as a surprise to CXOs and decision-makers as acceleration of AI adoption and proliferation of smart, intuitive and ML algorithms spawn the creation of new industries and business segments and overall, trigger new opportunities for business monetization. However, a few questions loom large for CXOs: How will these new industries and business segments be created with AI? And, what strategic shifts can leadership make to monetize these new business opportunities?
The creation of new industries and business segments depends on dramatic advances in AI that can take a swift adoption journey to move from discovery to commercial application to a new industry. New industry segments around AI are in the making and are far from tapped. A cursory look at new age businesses: Micro-segmented, hyper-personalized online shopping platforms, GPS driven ride-sharing companies, recommendation-driven streaming channels, adaptive learning based EdTech companies, conversational AI-driven new and work scheduling are just a few of the imminent and visible examples. Yet a lot more can be done in this space.
AI adoption brings intentional efforts to adapt to this onslaught of algorithms and how it’s affecting customer and employee behavior. As algorithms become a permanent fixture in everyday life, organizations are forced to update legacy technology strategies and supporting methodologies to better reflect how the real world is evolving. And the need to do so is becoming increasingly obligatory.
On the other side, traditional and incumbent enterprises are reverse engineering investments, processes, and systems to better align with how markets are changing. Because it’s focusing on customer behavior, AI is actually in its own way, making businesses more human. As such, Artificial Intelligence is not specifically about technology, it’s empowered by it. Without an end in mind, self-learning algorithms continually seek out how to use technology in ways that improve customer experiences and relationships. It also represents an effort that introduces new models for business and, equally, creates a way of staying in business as customers become increasingly aware and selective.
Today, AI expertise is focused more on developing commercial applications that optimize efficiencies in existing industries and is focused less on developing patented algorithms that could lead to new industries. These efficiencies are accelerating the sectoral consolidation and convergence, and are less about new industry creation.
However, AI’s most potent, long-term economic use may just be to augment the discovery and pursuit of solving large, complex and unresolved problems that could be the foundations of new industry segments. Enterprises have started realizing the significance of having a long-term strategic interest and investments in using AI in this way. Yet few of the above mentioned examples are testimony to AI triggering new industry segments and business opportunities. The real winners in the algorithm-driven economy will be business leaders that align their strategies to augment AI expertise from ground zero, keep a continuous tab on blockbuster algorithms, and redefine new business segments that enable monetization of new opportunities.
AI has immense potential to jumpstart the creation of new industries and the disruption of existing ones. The curation of this as a strategic roadmap for business leaders is far from easy, but it carries great rewards for businesses. It takes a village to bring about change, and it also takes the spark and perseverance of an AI strategist to spot important trends and create a sense of urgency around new possibilities.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Embark on AI@scale journey : Strategic Interventions for CXOs
Add Your Heading Text Here

AI is invoking shifts in the business value chains of enterprises. And it is redefining what it takes for enterprises to achieve competitive advantage. Yet, even as several enterprises have begun applying AI engagements with impressive results, few have developed full-scale AI capabilities that are systemic and enterprise wide.
The power of AI is changing business as we know it. AIQRATE AI@scale advisory services allow you to transform your operating model, so you can move beyond isolated AI use cases toward an enterprise wide program and realize the full value potential.
We have realized that that unleashing the true power of AI requires scaling it across the entire business functions and value chain and its calls for “transforming the business “.
An AI@scale transformation should occur through a series of top-down and bottom-up actions to create alignment, buy-in, and follow-through. This ensures the successful industrialization of AI across enterprises and their value chains.
The following strategic interventions are to be initiated to build AI@scale transformation program:
- AI Maturity Assessment: This strategic top-down establishes the overall context of the transformation and helps prevent the enterprises from pursuing isolated AI pilots. The maturity assessment is typically based on a blend of AI masterclass, surveys and assessments
- Strategic AI Initiatives and business value chains: This bottom-up step provides a baseline of current AI initiatives. It should include goals, business cases, accountabilities, work streams, and milestones in addition to an analysis of data management, algorithms, performance metrics. A review of the current business value chain and proposed transformational structure should also be conducted at this stage.
- Strategic mapping & gap Analysis: The next top-down step prioritizes AI initiatives, focusing on easy wins and low hanging fruits. This step also identifies the required changes to the operating business model.
- AI@scale transformation program: This critical strategic step consists of both the transformation roadmap, including the order of initiatives to be rolled out, and the creation of a planned program management approach to oversee the transformation.
- AI@scale implementation: This covers implementation, detailing the work streams, responsibilities, targets, milestones, talent and partner mapping.
By systematically moving through these steps, the implementation of AI@scale will proceed with much greater speed and certainty. Enterprises must be aware that AI@scale requires deep transformative changes and need strategic and operational buy ins from management for long term business gains and impact .
AIQRATE works closely with global & Indian enterprises , GCC’s , VC/PE firms to provide end-to-end AI@scale advisory services
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Reimagining the future of travel and hospitality with artificial intelligence
Add Your Heading Text Here

Over the years, the influence of artificial intelligence (AI) has spread to almost every aspect of the travel and the hospitality industry. Thirty percent of hospitality businesses use AI to augment at least one of their primary sales processes, and most customer personalisation is done using AI. The proliferation of AI in the travel and hospitality industry can be credited to the humongous amount of data being generated today. AI helps analyse data from obvious sources, brings value in assimilating patterns in image, voice, video, and text, and turns it into meaningful and actionable insights for decision making. Trends, outliers, and patterns are figured out using machine learning-based algorithms that help in guiding a travel or hospitality company to make informed decisions.
“Discounts, schemes, tour packages, and seasons and travellers to target are formulated using this intelligent data combined with behavioural science and social media attribution to know customers behaviour and insights. “
Let’s take a close look at the AI-driven application areas in the travel and hospitality industry and the impact on the ensuing business value chain:
Bespoke and curated experiences
There are always a few trailblazers who are up for a new challenge and adopt new-age exponential technologies. Many hotel chains have started using an AI concierge. One great example of an AI concierge is Hilton World wide’s Connie, the first true AI-powered concierge bot. Connie stands at two feet high and guests can interact with it during their check-in. Connie is powered by IBM’s Watson AI and uses the Way Blazer travel database. It can provide succinct information to guests on local attractions, places to visit, etc. Being AI-driven with self-learning ability, it can learn and adapt and respond to each guest on personalised basis.
In the travel business, Mezi, using AI with Natural Language Processing technique, provides a personalised experience to business travellers, who usually are strapped for time. It talks about bringing on a concept of bleisure (business+leisure) to address the needs of the workforce. The company’s research shows that 84 percent of business travellers return feeling frustrated, burnt out, and unmotivated. The kind of tedious and monotonous planning that goes into the travel booking could be the reason for it. With AI and NLP, Mezi collects individual preferences and generates personalised suggestions so that a bespoke and streamlined experience is given and the issues faced are addressed properly.
Intelligent travel search
Increased productivity now begins with the search for the hotel, and sophisticated AI usage has paved the way for the customer to access more data than ever before. Booking sites like Lola.com provides on-demand travel services and have developed algorithms that can not only instantly connect people to their team of travel agents who find and book flights, hotels, and cars, but have been able to empower their agents with tremendous technology to make research and decisions an easy process.
Intelligent travel assistants
Chatbot technology is another big strand of AI, and not surprisingly, many travel brands have already launched their own versions in the past year or so. Skyscanner is just one example, creating an intelligent bot to help consumers find flights in Facebook Messenger. Users can also use it to request travel recommendations and random suggestions. Unlike ecommerce or retail brands using chatbots, which can appear gimmicky, there is an argument that examples like Skyscanner are much more relevant and useful for everyday consumers. After all, with the arrival of many more travel search websites, consumers are being overwhelmed by choice – not necessarily helped by it. Consequently, a chatbot like Skyscanner is able to cut through the noise, connecting with consumers in their own time and in the social media spaces they most frequently visit.
Recently, Aero Mexico started using Facebook Messenger chatbot to answer very generic customer questions. The main idea was to cater to 80 percent of questions, which are usually repeat ones and about common topics. Thus, AI is of great application to avoid a repetitive process. Airlines hugely benefit from this. KLM Royal Dutch Airlines uses AI to respond to the queries of customers on Twitter and Facebook. It uses an algorithm from a company called Digital Genius, which is trained on 60,000 questions and answers. Not only this, Deutsche Lufthansa’s bot Mildred can help in searching the cheapest fares.
Intelligent recommendations
International hotel search engine Trivago acquired Hamburg, Germany machine learning startup Tripl as it ramps up its product with recommendation and personalisation technology, giving them a customer-centric approach. The AI algorithm gives tailored travel recommendations by identifying trends in users’ social media activities and comparing it with in-app data of like-minded users. With its launch, users could sign up only through Facebook, potentially sharing oodles of profile information such as friends, relationship status, hometown, and birthdays.
Persona-based travel recommendations, use of customised pictures and text are now gaining ground to entice travel. KePSLA’s travel recommendation platform is one of the first in the world to do this by using deep learning and NLP solutions. With 81 percent of people believing that intelligent machines would be better at handling data than humans, there is also a certain level of confidence in this area from consumers.
Knowing your traveller
Dorchester Collection is another hotel chain to make use of AI. However, instead of using it to provide a front-of-house service, it has adopted it to interpret and analyse customer behaviour deeply in the form of raw data. Partnering with technology company, Richey TX, Dorchester Collection has helped to develop an AI platform called Metis.
Delving into swathes of customer feedback such as surveys and reviews (which would take an inordinate amount of time to manually find and analyse), it is able to measure performance and instantly discover what really matters to guests. Métis helped Dorchester to discover that breakfast it not merely an expectation – but something guests place huge importance on. As a result, the hotels began to think about how they could enhance and personalise the breakfast experience.
Intelligent forecasting: flight fares and hotel tariffs
Flight fares and hotel tariffs are dynamic and vary on real-time basis, depending on the provider. No one has time to track all those changes manually. Thus, intelligent algorithms that monitor and send out timely alerts with hot deals are currently in high demand in the travel industry.
Trivago and Make my trip are screening through swamp of data points, variables, and demand and supply patterns to recommend optimised travel and hotel prices. The AltexSoft data science team has built such an innovative fare predictor tool for one of their clients, a global online travel agency, Fareboom.com. Working on its core product, a digital travel booking website, they could access and collect historical data about millions of fare searches going back several years. Armed with such information, they created a self-learning algorithm, capable of predicting future price movements based on a number of factors, such as seasonal trends, demand growth, airlines special offers, and deals.
Optimised disruption management: delays and cancellations
While the previous case is focused mostly on planning trips and helping users navigate most common issues while traveling, automated disruption management is somewhat different. It aims at resolving actual problems a traveller might face on his/her way to a destination point. Mostly applied to business and corporate travel, disruption management is always a time-sensitive task, requiring instant response.
While the chances of getting impacted by a storm or a volcano eruption are very small, the risk of a travel disruption is still quite high: there are thousands of delays and several hundreds of cancelled flights every day. With the recent advances in AI, it became possible to predict such disruptions and efficiently mitigate the loss for both the traveller and the carrier. The 4site tool, built by Cornerstone Information Systems, aims to enhance the efficiency of enterprise travel.
The product caters to travellers, travel management companies, and enterprise clients, providing a unique set of features for real-time travel disruption management. In an instance, if there is a heavy snowfall at your destination point and all flights are redirected to another airport, a smart assistant can check for available hotels there or book a transfer from your actual place of arrival to your initial destination.
Not only are passengers are affected by travel disruptions; airlines bear significant losses every time a flight is cancelled or delayed. Thus, Amadeus, one of the leading global distribution systems (GDS), has introduced a Schedule Recovery system, aiming to help airlines mitigate the risks of travel disruption. The tool helps airlines instantly address and efficiently handle any threats and disruptions in their operations.
Future potential: So, reflecting on the above-mentioned use cases of the travel and hospitality industry leveraging Ai to a large extent, there will be few latent potential areas in the industry that will embrace AI in the future :
“Undoubtedly, we will witness many travel and hospitality organisations using AI for intelligent recommendations as well as launching their own chatbots. There’s already been a suggestion that Expedia is next in line, but it is reportedly set to focus on business travel rather than holidaymakers.”
Due to the greater need for structure and less of a desire for discovery, it certainly makes sense that AI would be more suited to business travellers. Specifically, it could help to simplify the booking process for companies, and help eliminate discrepancies around employee expenses. With reducing costs and improving efficiency two of the biggest benefits, AI could start to infiltrate business travel even more so than leisure in the next 12 months.
Lastly, we can expect to see greater development in conversational AI in the industry. With voice-activated search, the experience of researching and booking travel has the potential to become quicker and easier than ever before. Similarly, as Amazon Echo and Google Home start to become commonplace, more hotels could start to experiment with speech recognition to ramp up customer service. This means devices and bots could become the norm for brands in the travel and hospitality industry.
The travel and hospitality industry transformation will morph into experience-driven and asset-light business, and wide adoption of AI will usher a new-age customer experience and set a benchmark for other industries to emulate. Fasten your seat belts … AI will redefine the travel and hospitality industry.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS
How India can Emerge as a Premier Destination for AI; Watch out China, USA…
Add Your Heading Text Here

This detailed primer will provide you crucial overview of the AI’s increasing prevalence amongst Indian industry, government and peripheral ecosystem and the significant impact AI will have in your organizations to remodel strategic and business models accordingly. The ensuing details also highlights the relative comparison amongst India, China and USA on the steady progress being done in AI adoption.
VC’s, PE funds and investors attempting to understand where to target investment, what offerings and capabilities would lead to better performance and gains, and how to capitalize on AI opportunities, it’s crucial for them to understand the International economic potential of AI for now and projections in the coming years.
Cutting across all these considerations is how to build responsible AI operating models and keep it transparent enough to maintain the confidence of customers and wider stakeholders.
International AI Capitalization Report – China & NA Leads, India hot in the heels
Without doubt, AI is going to be a big game changer in the international setting. A recent PwC report concludes that AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy in 2030, more than the current output of China and India combined. Of this, $6.6 trillion is likely to come from increased productivity and $9.1 trillion is likely to come from consumption-side effects.
Global GDP will be up to 14% higher in 2030 as a result of the accelerating development and take-up of AI
from the standpoint of direct economic impact of AI, China and North America will have greatest gains in GDP. Even though NA will reach its peak of AI led growth faster due to huge opportunities in parallel technologies implementations and advanced customer readiness for AI. NA is supposed to reach the peak of macroeconomic gains by 2020, following which there would be a relative slowdown in the growth.

Figure 1: Souce – PwC Analysis
China, on the other hand will have a slower but stable rise in GDP gains, even post mid 2020s because a large portion of Chinese GDP comes from manufacturing, a sector which is highly susceptible to AI disruption in its operation, and also a higher rate of capital re-investment within Chinese economy compared to EU and NA. As productivity in China eventually catches up with North America, NA will focus more on importing AI-enabled products from China due to economically cheap alternative China provides. Hence by 2030, China will see much larger impact in its GDP.
Sector-wise AI Consumption Impact Index – The sector-wise impact of AI and its constituent offerings space will give crucial overview for investors to get a clear understanding of opportunities and threats in AI investment space. AI is set to be the key source of transformation, disruption and competitive advantage in today’s fast changing economy. Drawing on the findings of our AI Impact Index, we look at how quickly change is coming and where your business can expect the greatest return.

Figure 2: AI Consumption Impact (Src: PwC Analysis)
Deriving from the detailed PwC analysis report, which includes an AI impact index rating which gives an indication of enhancing quality and personalization for consumers and freeing up their time to invest their preferences in other endeavours.
The areas with the biggest potential representation will help your business target investment in the short to medium term. Some aspects could be even more disruptive or even revolutionary, such as robotic doctors, but they would be further off in the timeline of mainstream implementation.
Is the Differential for Developing countries like India too steep in catching up with AI? – AI is still at its early stages, which means that irrespective of the fact that the technology landscape is skewed towards the developed economies as compared to developing, the developing economies and their markets could still lead the developed markets from AI standpoint. This makes countries like India, the second largest economy with a strong focus in IT sector, a strong contender.
The economic impact of AI in GDP for developing countries, will be driven by:
- Productivity gains from businesses automating processes (including use of robots and autonomous vehicles).
- Productivity gains from businesses augmenting their existing labour force with AI technologies (assisted and augmented intelligence).
- Increased consumer demand resulting from the availability of personalised and/or higher-quality AI-enhanced products and services.
The consumer revolution set off by AI opens the way for massive disruption as both established businesses and new entrants drive innovation and develop new business models. A key part of the impact of AI will come from its ability to make the most of parallel developments such as IoT connectivity.
India’s Macroeconomic Landscape of AI
India is already way ahead of many other countries in implementing artificial intelligence (AI). More than half of the companies are going beyond pilot and test projects and adopting the technology at a larger scale. This statistic is largely driven by American firms such as Accenture, Microsoft, the successful implementers’ toolkit, said. Last year, India was the second-largest global site for new centres, after the US.
Well over 58% of the companies that are using AI in India are working with the technology at significant scale
The Indian government’s Digital India initiative, too, has created a favourable regulatory environment for increased use of AI.
Recipe for AI Success in India – Digital & Data Bedrock
As India undergoes rapid digital transformation, data centres and the intelligence behind the data collected will enable the government and industry to make effective decisions based on algorithms. This means increasing opportunities for using (and investing over) AI in the country.
For example, Intel is betting on Artificial Intelligence (AI) to drive demand for its electronic chips, for which it is aiming to train 15,000 scientists, developers, engineers and students on AI in India over the next one year. The company will host 60 courses under its ‘AI Developer Education Program’. These will train people on ways they can adopt AI for better research, testing or even building of products. Intel is looking at India due to the country’s large base of technical talent. The country is the third largest global site for AI companies.
As India’s largest e-commerce marketplace Flipkart closes in on completing a decade in the business, it is looking to put in use its mammoth pile of data to predict sales of products months in advance. The company is working on an artificial intelligence (AI) solution that will give it an edge over rivals by helping it make smarter decisions in ordering, distribution and pricing products on its platform. Ultimately, the AI system will allow Flipkart to boost efficiency and reduce the cost of products for customers.
While rival Amazon, which has around a 10-year headstart over Flipkart, is known to have some of the most advanced sales prediction engines, the Indian company has the advantage of having a bigger data set of the country’s online consumer market.
AI Inroads in the Private Sector
AI has now a significant impact in the day to day lives of the regular mass of the country. Now that the Indian IT sector has reached a certain intermediary peak of digitization, the focus, now , is more on automating the repetitive problems and finding more optimized, efficient or refined methods of performing the same tasks, with less time duration and lesser manpower. The result is the standardization of some very critical app based services like virtual assistants, cab aggregators, shopping recommendations etc. This will eventually lead to AI solutions to real world problems.
The AI Startups Sphere of India- Startups are clearly playing a major role in innovating faster than corporates, which has led to several curious partnerships. SAP India has invested in Niki.ai, a bot that improves the ordering experience. Then there’s Ractrack.AI, where a bot improves customer engagement and provides insights; it functions as a virtual communications assistant to convert the customer into a client. Racetrack is helping companies turn leads into meaningful engagements by using AI. Another startup, LUCEP, converts all potential queries into leads with their AI engine.
The objective is to generate insights from data and simplify customer interaction with a business and also convert them into leads.
Indian startups saw $4 billion in risk capital being deployed across 1,040 angel and VC/PE deals between January and December 2016.
Disclosed funding announcements have shown a decreased value of 55 percent from the same period last year (2015) and a decrease of 20 percent from 2014. About $9 billion in VC/PE capital had been invested in 2015. The number of deals in 2016, however, has increased by 3 percent over the last year. On an average, four startup deals were announced every weekday throughout 2016. VCs predict that going forward machine learning and AI would be key themes to invest in.
AI in Public Sector– Ripe for Digital Revamp and AI Adoption
A Blue Ocean for AI Investment due to Digital India Initiatives – Though both corporates and startups are making significant inroads in instituting AI in their service architecture and product offerings, and sometimes as part of their core business strategy itself, the challenges in the public sector in instituting AI can be quickly overcome due to huge Digital Movements instituted by the Indian Govt. like Digital India, Skill India and Make in India. This will create a solid bedrock of Data and Digital Footprint which will act as a foundational infrastructure to base AI implementation on, opening a huge blue ocean in public sector, rich for AI investment.
A New Workaround for Regulatory Challenges in Public Sector AI Implementation – One of the peculiar problems the public sector faces in mainstream implementation of AI is the fact that since AI is a continuously self-learning system, capable of analytical or creative decision making and autonomous implementation of actions, who will then be accountable in taking responsibility for its actions, should they turn out to be not so favourable. This is because of the fact that since AI has a degree of autonomous decision making, it makes it difficult to pre-meditate its consequence. The AI systems are meant to augment and enrich the life of the consumers. In such a situation, deciding liability of AI system’s actions will be difficult. Therefore, a lot of deliberation will be required to carefully come to a precise conclusion surrounding implementing these systems with ethical foundation and propriety.
Although many countries like US and some European countries are in the verge of implementing regulations and laws surrounding concepts like driverless vehicles, India still don’t have the regulations sanctioned. This, but need not be a bad news. India is cut to establish a completely revamped legal infrastructure, thereby completely circumventing the need for continuous regulatory intervention. Also, there is a favourable atmosphere in India as far as AI is concerned which will foster a spike in activities in that avenue.
Indian Governance Initiatives – Huge Scope for Investment of AI – As India emerges as a premier destination for AI, scope for investment opens in the governance aspect, in several ways. Governance schemes have a unique trait of the baggage of large volume and large scale implementation need, which can be tackled with Deep learning. For example, in Swachh Bharat Initiative, specifically construction of toilets in rural India, public servants are tasked with uploading images of these toilet constructions to a central server for assessment. Image recognition can be used to target unfinished toilets. It can also be used to identify whether the same official appears in multiple images or if photos were uploaded from a different location other than the intended place.
Other initiatives such as the Make in India, Digital India & Skill India can be augmented with AI to deal with scale. The range of application for AI techniques could range from crop insurance schemes, tax fraud detection, and detecting subsidy leakage and defence and security strategy.
An AI system can improve and enrich the agriculture of India by enhancing the bodies like The Department of Agriculture Cooperation and Farmers Welfare, Ministry of Agriculture runs the Kisan Call Centers across the country etc. It can help assist the call centre by linking various available information like soil reports from government agencies and link them to the environmental conditions. It will then provide advice on the optimal crop that can be sown in that land pocket.
As the need for large scale implementation and monitoring of governance initiative becomes more pronounced, the need for AI becomes absolute and it will open doors to considerable AI investment in the future of India.
Finally, Looking Ahead – A Collaborative Innovation Environment due to AI
AI innovations which fall under assisted, augmented and autonomous intelligence will help users understand and decide which level of intelligence is helpful and required in their context, thereby making AI Acceptance easier for the people. At the same time, this AI continuum can be used to understand economic ramifications, usage complexity and decision-making implications. While academia and the private sector conduct research on various AI problems with diverse implications in mind, the public sector with its various digital initiatives (Digital India, Make in India, etc.) can identify areas where parts of the AI continuum can be utilised to increase reach, effectiveness and efficiency, thereby giving direction to AI Innovative Research.
A collaborative innovation environment between academia and the private and public sectors will help provide holistic and proactive advisory delivery to the population, for eg. through public call centres, linking information from various government sources. At the same time, the rich data generated from these interactions can be used to draw deep conclusions. Collaboration between the three pillars could further help get a comprehensive view of problems and find intelligent and innovative ways to increase the efficiency and effectiveness of services delivered to society.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Travel & Hospitality Industry Transformation: Served Fast with AI
Add Your Heading Text Here

Over the years, the influence of AI has spread to almost every aspect of the travel and the hospitality industry. 30% of hospitality businesses use artificial intelligence to augment at least one of their primary sales processes and most customer personalization is done using AI.
30% of hospitality businesses use artificial intelligence to augment at least one of their primary sales processes.
The sudden popularity of Artificial Intelligence in the Travel industry can be credited to the humongous amount of data being generated today. Artificial Intelligence helps analyse unstructured data, brings value in partnership with Big Data and turns it into meaningful and actionable insights. Trends, outliers and patterns are figured out using this smart data which helps in guiding a Travel company to make informed decisions. The discounts, schemes, tour packages, seasons to target and people to target are formulated using this data. Usually, surveys and social media sensing are done to know customer’s insights and behaviour.
Let’s look at how AI has influenced each aspect of the business
Bleisure – Personalized Experience
There are always a few who are up for a new challenge and adopt to new technology. Many hotels have started using an AI concierge. One great example of an AI concierge is Hilton World wide’s Connie, who is the first true AI-powered concierge bot.
Connie stands at 2 feet high and guests can interact with it during their check-in. Connie is powered by IBM’s Watson AI and uses WayBlazer travel database. It can provide information to guests on local attractions, places to visit, etc. Being an AI, it can learn and adapt and respond to each guest.
In the Travel business, Mezi, using Artificial Intelligence and Natural Language Processing, provides a personalized experience to Business travellers who usually are strapped for time. It talks about bringing on a concept of bleisure (business+leisure) to address the needs of the workforce. A research done by them states that 84% of business travellers return feeling frustrated, burnt out and unmotivated. The kind of tedious and monotonous planning that goes into the travel booking could be the reason for it. With AI and NLP, Mezi collects preferences and generates suggestions so that a customized and streamlined experience is given and the issues faced by them are addressed properly.
Increased Productivity – Instant Connectivity
Increased productivity now begins with the search for the hotel, and technology has paved its way for the customer to access more data than ever before. Booking sites like Lola (www.lola.com) who provide on-demand travel services have developed technologies that can not only instantly connects people to their team of travel agents who find and book flights, hotels, and cars but have been able to empower their agents with tremendous technology to make research and decisions an easy process.
Intelligent Travel Assistants – Chatbots
Chatbot technology is another big strand of AI, and unsurprisingly, many travel brands have already launched their own versions in the past year or so. Skyscanner is just one example, creating a bot to help consumers find flights in Facebook Messenger. Users can also use it to request travel recommendations and random suggestions. Unlike ecommerce or retail brands using chatbots, which can appear gimmicky, there is an argument that examples like Skyscanner are much more relevant and useful for everyday consumers.
After all, with the arrival of many more travel search websites, consumers are being overwhelmed by choice – not necessarily helped by it. Consequently, a bot like Skyscanner is able to cut through the noise, connecting with consumers in their own time and in the social media spaces they most frequently visit.
Recently, Aeromexico started using Facebook Messenger chatbot to answer the very generic questions by the customers. The main idea was to cater to 80% of questions which are usually the repeated ones and about common topics. Thus, to avoid a repetitive process, artificial intelligence is of great application. Airlines hugely benefit from this. KLM Royal Dutch Airlines uses artificial intelligence to respond to the queries of customers on twitter and facebook. It uses an algorithm from a company called Digital Genius which is trained on 60,000 questions and answers. Not only this, Deutsche Lufthansa’s bot Mildred can help in searching the cheapest fares.
Discovery & Data Analysis – Intelligent Recommendations
International hotel search engine Trivago acquired Hamburg, Germany machine learning startup, Tripl, as it ramps up its product with recommendation and personalization technology, giving them a customer-centric approach.
The AI algorithm gives tailored travel recommendations by identifying trends in users’ social media activities and comparing it with in-app data of like-minded users. With its launch in July 2015, users could sign up only through Facebook, potentially sharing oodles of profile information such as friends, relationship status, hometown, and birthday.
Persona based travel recommendations, use of customised pictures and text are now gaining ground to entice travellers to book your hotels. KePSLA’s travel recommendation platform is one of the first in the world to do this by using deep learning and NLP solutions.
With 81% of people believing that robots would be better at handling data than humans, there is also a certain level of confidence in this area from consumers.
Knowing your Travellers – Deep Customer Behaviour
Dorchester Collection is another hotel chain to make use of AI. However, instead of using it to provide a front-of-house service, it has adopted it to interpret and analyse customer behaviour in the form of raw data.
Partnering with technology company, RicheyTX, Dorchester Collection has helped to develop an AI platform called Metis.
Delving into swathes of customer feedback such as surveys and reviews (which would take an inordinate amount of time to manually find and analyse) it is able to measure performance and instantly discover what really matters to guests.
For example, Metis helped Dorchester to discover that breakfast it not merely an expectation – but something guests place huge importance on. As a result, the hotels began to think about how they could enhance and personalise the breakfast experience.
Flight Fare and Hotel Price Forecasting
Flight fares and hotel prices are ever-changing and vary greatly depending on the provider. No one has time to track all those changes manually. Thus, smart tools which monitor and send out timely alerts with hot deals are currently in high demand in the travel industry.
The AltexSoft data science team has built such an innovative fare predictor tool for one of their clients, a global online travel agency, Fareboom.com. Working on its core product, a digital travel booking website, they could access and collect historical data about millions of fare searches going back several years. Armed with such information, they created a self-learning algorithm, capable of predicting the future price movements based on a number of factors, such as seasonal trends, demand growth, airlines special offers, and deals.
With the average confidence rate at 75 percent, the tool can make short-term (several days) as well as long-term (a couple of months) forecasts.
Optimized Disruption Management
While the previous case is focused mostly on planning trips and helping users navigate most common issues while traveling, automated disruption management is somewhat different. It aims at resolving actual problems a traveler might face on his/her way to a destination point.
Mostly applied to business and corporate travel, disruption management is always a time-sensitive task, requiring instant response. While the chances to get impacted by a storm or a volcano eruption are very small, the risk of a travel disruption is still quite high: there are thousands of delays and several hundreds of canceled flights every day.
With the recent advances in technology, it became possible to predict such disruptions and efficiently mitigate the loss for both the traveler and the carrier. The 4site tool, built by Cornerstone Information Systems, aims at enhancing the efficiency of enterprise travel. The product caters to travelers, travel management companies, and enterprise clients, providing a unique set of features for real-time travel disruption management.
For example, if there is a heavy snowfall at your destination point and all flights are redirected to another airport, a smart assistant can check for available hotels there or book a transfer from your actual place of arrival to your initial destination.
Not only passengers are affected by travel disruptions; airlines bear significant losses every time a flight is canceled or delayed. Thus, Amadeus, one of the leading global distribution systems (GDS), has introduced Schedule Recovery system, aiming to help airlines mitigate the risks of travel disruption. The tool helps airlines instantly address and efficiently handle any threats and disruptions in their operations.
Future potential
So, we’ve already seen the travel industry capitalise on AI to a certain extent. But how will it evolve in the coming year?
Business travel
Undoubtedly, we’ll see many more brands using AI for data analysis as well as launching their own chatbots. There’s already been a suggestion that Expedia is next in line, but it is reportedly set to focus on business travel rather than holidaymakers. Due to the greater need for structure and less of a desire for discovery, it certainly makes sense that artificial intelligence would be more suited to business travellers.
Specifically, it could help to simplify the booking process for companies, as well as help eliminate discrepancies around employee expenses. With reducing costs and improving efficiency two of the biggest benefits, AI could start to infiltrate business travel even more so than leisure in the next 12 months.
Voice technology
Lastly, we can expect to see greater development in voice-activated technology.
With voice-activated search, the experience of researching and booking travel has the potential to become quicker and easier than ever before. Similarly, as Amazon Echo and Google Home start to become commonplace, more hotels could start to experiment with speech recognition to ramp up customer service.
This means devices and bots could become the norm for brands in the travel industry.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Fluid Supply Chain Transformation = AI + Automation
Add Your Heading Text Here

Rapidly evolving technology and a digitally focused world have opened the door for a new wave of automation to enter the workforce. Robots already stand side-by-side with their human counterparts on many manufacturing floors, adding efficiency, capacity (robots don’t need to sleep!) and dependability. Add in drones and self-driving vehicles and it’s no wonder many are questioning the role of humans going forward.
Supply chains, although automated to a degree, still face challenges brought about by the amount of slow, manual tasks required, and the daily management of a complex web of interdependent parts. The next generation of process efficiency gains and visibility could be on your doorstep with artificial intelligence in supply chain management, if only you’d let the robots automatically open it for you.
Robotic Process Automation
RPA works by automating the end-to-end supply chain, enabling the management of all tasks and sections in tandem. It allows you to spend less time on low value, high frequency activities like managing day-to-day processes, and provides more time to work on high value, exception-based requirements, which ultimately drives value for the entire business.
PwC estimates businesses could automate up to 45% of current work, saving $2 trillion in annual wages. “In addition to the cost and efficiency advantages, RPA can take a business to the next level of productivity optimization,” the firm says. Those ‘lights out’ factories and warehouses are becoming closer to a reality.
Four key elements need to be in place for you to take full advantage of robotic process automation in your supply chain:
- robots for picking orders and moving them through the facility;
- sensors to ensure product quality and stock;
- cognitive learning systems;
- and, artificial intelligence to turn processes into algorithms to guide the entire operation.
In addition, you’ll need strong collaboration internally and among suppliers and customers to tie all management systems back to order management and enterprise resource planning platforms.
Artificial Intelligence In Supply Chain Automation
AI is changing the traditional way in which companies are operating. Siemens in its “lights out” manufacturing plant, has automated some of its production lines to a point where they are run unsupervised for several weeks.
Siemens is also taking a step towards a larger goal of creating Industrie 4.0 or a fully self-organizing factory which will automate the entire supply chain. Here, the demand and order information would automatically get converted into work orders and be incorporated into the production process.
This would streamline manufacturing of highly customized products.
Artificial Intelligence In Supplier Management And Customer Service
Organizations are also increasingly leveraging AI for supplier management and customer management. IPsoft’s AI platform, Amelia automates work knowledge and is able to speak to the customers in more than 20 languages. A global oil and gas company has trained Amelia to help provide prompt and more efficient ways of answering invoicing queries from its suppliers. A large US-based media services organization taught Amelia how to support first line agents in order to raise the bar for customer service.
Artificial Intelligence In Logistics & Warehousing
Logistics function will undergo a fundamental change as artificial intelligence gets deployed to handle domestic and international movement of goods. DHL has stated that its use of autonomous fork lifts is “reaching a level of maturity” in warehouse operations. The next step would be driver less autonomous vehicles undertaking goods delivery operations.
Artificial Intelligence In Procurement
AI is helping drive cost reduction and compliance agenda through procurement by generating real time visibility of the spend data. The spend data is automatically classified by AI software and is checked for compliance and any exceptions in real time. Singapore government is carrying out trials of using artificial intelligence to identify and prevent cases of procurement fraud.
The AI algorithm analyzes HR and finance data, procurement requests, tender approvals, workflows, non-financial data like government employee’s family details and vendor employee to identify potentially corrupt or negligent practices. AI will also take up basic procurement activities in the near future thereby helping improve the procurement productivity.
Artificial Intelligence in new product development
AI has totally overhauled the new product development process.by reducing the time to market for new products. Instead of developing physical prototypes and testing the same, innovators are now creating 3D digital models of the product. AI facilitates interaction of the product developers in the digital space by recognizing the gestures and position of hand. For example, the act of switching on a button of a digital prototype can be accomplished by a gesture.
AI In Demand Planning And Forecasting
Getting the demand planning right is a pain point for many companies. A leading health food company leveraged analytics with machine learning capabilities to analyze their demand variations and trends during promotions.
The outcome of this exercise was a reliable, detailed model highlighting expected results of the trade promotion for the sales and marketing department. Gains included a rapid 20 percent reduction in forecast error and a 30 percent reduction in lost sales.
AI in Smart Logistics
The impact of data-driven and autonomous supply chains provides an opportunity for previously unimaginable levels of optimization in manufacturing, logistics, warehousing and last mile delivery that could become a reality in less than half a decade despite high set-up costs deterring early adoption in logistics.
Changing consumer behavior and the desire for personalization are behind two other top trends Batch Size One and On-demand Delivery: Set to have a big impact on logistics, on-demand delivery will enable consumers to have their purchases delivered where and when they need them by using flexible courier services.
A study by MHI and Deloitte found more than half (51%) of supply chain and logistics professionals believe robotics and automation will provide a competitive advantage. That’s up from 39% last year. While only 35% of the respondents said they’ve already adopted robotics, 74% plan to do so within the next 10 years. And that’s likely in part to keep up with key players like Amazon, who have been leading the robotics charge for the past few years.
What is the mantra ?
These examples showcase that in today’s dynamic world, AI embedded supply chains offer a competitive advantage. AI armed with predictive analytics can analyze massive amounts of data generated by the supply chains and help organizations move to a more proactive form of supply chain management.
Thus, in this digital age where the mantra is “evolve or be disrupted”, companies are leveraging AI to reinvent themselves and scale their businesses quickly. AI is becoming a key enabler of the changes that businesses need to make and is helping them manage complexity of the constant digital change.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

The Rush for Artificial Intelligence in Silicon Valley…Is This Here to Stay?
Add Your Heading Text Here

For more than a decade, Silicon Valley’s technology investors and entrepreneurs obsessed over social media and mobile apps that helped people do things like find new friends, fetch a ride home or crowdsource a review of a product or a movie.
Robots after the “Like” Button
Now Silicon Valley has found its next shiny new thing. And it does not have a “Like” button.
The new era in Silicon Valley centers on artificial intelligence and robots, a transformation that many believe will have a payoff on the scale of the personal computing industry or the commercial internet, two previous generations that spread computing globally. Computers have begun to speak, listen and see, as well as sprout legs, wings and wheels to move unfettered in the world.
The shift was evident in a Lowe’s home improvement store here this month, when a prototype inventory checker developed by Bossa Nova Robotics silently glided through the aisles using computer vision to automatically perform a task that humans have done manually for centuries.
The robot, which was skilled enough to autonomously move out of the way of shoppers and avoid unexpected obstacles in the aisles, alerted people to its presence with soft birdsong chirps. Gliding down the middle of an aisle at a leisurely pace, it can recognize bar codes on shelves, and it uses a laser to detect which items are out of stock.
Silicon Valley’s financiers and entrepreneurs are digging into artificial intelligence with remarkable exuberance. The region now has at least 19 companies designing self-driving cars and trucks, up from a handful five years ago. There are also more than a half-dozen types of mobile robots, including robotic bellhops and aerial drones, being commercialized.
The Surge after the Static – The Social Way
There has been a slow trickle in investments in robotics all this while, and suddenly, there seem to be a dozen companies securing large investment rounds focusing on specific robotic niches. Funding in A.I. start-ups has increased more than fourfold to $681 million in 2015, from $145 million in 2011, according to the market research firm CB Insights. The firm estimates that new investments will reach $1.2 billion this year, up 76 percent from last year.
By contrast, funding for social media start-ups peaked in 2011 before plunging. That year, venture capital firms made 66 social media deals and pumped in $2.4 billion. So far this year, there have been just 10 social media investments, totaling $6.9 million, according to CB Insights. Last month, the professional social networking site LinkedIn was sold to Microsoft for $26.2 billion, underscoring that social media has become a mature market sector.
Even Silicon Valley’s biggest social media companies are now getting into artificial intelligence, as are other tech behemoths. Facebook is using A.I. to improve its products. Google will soon compete with Amazon’s Echo and Apple’s Siri, which are based on A.I., with a device that listens in the home, answers questions and places e-commerce orders. Satya Nadella, Microsoft’s chief executive, recently appeared at the Aspen Ideas Conference and called for a partnership between humans and artificial intelligence systems in which machines are designed to augment humans.
The auto industry has also set up camp in the valley to learn how to make cars that can do the driving for you. Both technology and car companies are making claims that increasingly powerful sensors and A.I. software will enable cars to drive themselves with the push of a button as soon as the end of this decade — despite recent Tesla crashes that have raised the question of how quickly human drivers will be completely replaced by the technology.
AI Outdoes the Silicon Valley Reset Trend
Silicon Valley’s new A.I. era underscores the region’s ability to opportunistically reinvent itself and quickly follow the latest tech trend. This is at the heart of the region’s culture that goes all the way back to the Gold Rush. The valley is built on the idea that there is always a way to start over and find a new beginning.
The change spurred a rush for talent in A.I. that has become intense. It is unusual that the number of people trying to get the students to drop out of the class halfway through because now they know a little bit of this stuff is crazy. The valley’s tendency toward reinvention dates back to the region’s initial emergence from the ashes of a deep aerospace industry recession as a consumer-electronics manufacturing center producing memory chips, video games and digital watches in the mid-1970s. A malaise in the personal computing market in the early 1990s was followed by the World Wide Web and the global expansion of the consumer internet.
A decade later, in 2007, just as innovation in mobile phones seemed to be on the verge of moving away from Silicon Valley to Europe and Asia, Apple introduced the first iPhone, resetting the mobile communications marketplace and ensuring that the valley would — for at least another generation — remain the world’s innovation center.
In the most recent shift, the A.I. idea emerged first in Canada in the work of cognitive scientists and computer scientists like Geoffrey Hinton, Yoshua Bengio and Yann LeCun during the previous decade. The three helped pioneer a new approach to deep learning, a machine learning method that is highly effective for pattern recognition challenges like vision and speech. Modeled on a general understanding of how the human brain works, it has helped technologists make rapid progress in a wide range of A.I. fields.
The Road Ahead
How far the A.I. boom will go is hotly debated. For some technologists, today’s technical advances are laying the groundwork for truly brilliant machines that will soon have human-level intelligence. Yet Silicon Valley has faced false starts with A.I. before. During the 1980s, an earlier generation of entrepreneurs also believed that artificial intelligence was the wave of the future, leading to a flurry of start-ups. Their products offered little business value at the time, and so the commercial commercial enthusiasm ended in disappointment, leading to a period now referred to as the “A.I. Winter.” The current resurgence will not fall short this time, and the economic potential in terms of new efficiency and new applications is strong.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Chatbots – The Protege of AI & Data Sciences
Add Your Heading Text Here

There has been a great deal of talk about the use of Artificial Intelligence chatbots in the last few weeks, especially given the news that Facebook are looking to implement AI into their Messenger and WhatsApp platforms, which are currently used by more than 1.8 billion people worldwide. However, does this bode well for the relationship between humans and Artificial Intelligence programs? Would you rather speak to an intelligent algorithm rather than a fellow human being?
The Sales and Customer Support Bot-ler ?
Chatbots, done right, are the cutting-edge form of interactive communications that captivate and engage users. But what kind of potential do they have for sales & customer support ?
To answer this, I should emphasize that customer service can be a delicate field. A lot of consumer engagement with a company happens when something goes wrong — such as a recently-purchased broken product or an incorrect bill or invoice.
By nature, these situations can be highly emotional. And as a business, you want to be responsive to potentially problematic customer inquiries like these. So relying on a chatbot to resolve issues that require a human touch might not be the best idea.
This is especially true if you let your bot “learn” from interactions it sees (say, in user forums) with no or minimal supervision. Things can easily go wrong, as the disaster around Microsoft’s Twitter bot “Tay” showed.
On the other hand, with the right supervision and enough training data, machine learning as an A.I. technique can help build very responsive and accurate informational chatbots — for example those that are meant to help surface data from large text collections, such as manuals.
I’d say that machine learning as a technique has been shown to work best on image processing. The advancements that Google, Facebook, and innovative startups such as Moodstocks (just acquired by Google) are showing in that space are truly amazing. Part of the amazement however, comes from the fact that we now see software take on another cognitive task that we thought could only be managed by humans.
What can bots do for the bottom line?
In my opinion, a bot’s primary application lies in customer service since most companies unfortunately continue to rely on an ancient methodology to manage customer interaction. And this is to be expected as most consumers themselves are still “hard-wired” to pick up a phone and dial a number when they want to engage with a company.
Companies haven’t necessarily made it easy for consumers to transition to digital-first interaction. Consumers are forced to either download a mobile app, browse websites, or use voice, the “dumbest” channel the smartphone has to offer, to retrieve information or perform transactions.
This is truly unfortunate because when it comes to paying a bill, checking on an order status, or reviewing account transactions, nothing is easier than sending a simple message. And with 900 million users now on Facebook Messenger, 1 billion on WhatsApp, and hundreds of millions more on basic SMS, companies have a consumer-preferred new medium for engaging with customers.
With messaging, a simple question can be posed in a simple message such as “Where is my order?”
Contrast this to the conventional options of being forced to shepherding that question through a maze of web or mobile app menus, or with IVR systems over the phone. Now imagine how a consumer-adopted, digital and automated interaction for simple questions vs. agent interaction over the phone could impact customer service and its cost. When chatbots handle the most commonly-asked questions, agent labor is reduced or redeployed to manage more complex and time-consuming interactions. Simple and moderate issues are resolved faster, leading to greater customer satisfaction and long-term loyalty. Bots can help deflect calls from the contact center and your IVR, which further reduces speech recognition license and telephony cost.
Could there be Bot-tle-necks?
There is also the question of whether these chatbots will take jobs from humans; a subject of fierce debate for all industries and levels in the last few months. Facebook itself has been quick to clarify that these chatbots are not going to replace the people in their organisation, but instead to work alongside them. For example, Facebook have said that the customer service executives will be required to train the AI bots, and to step in when the AI comes unstuck, which is likely to be fairly frequently in the early stages! Chinese messenger service WeChat has taken the chatbot idea on, with companies having official accounts through which they are able to communicate with their customers. However, the platform is still in its early stages, and is reported to be incredibly frustrating to use, so those in the customer service sector needn’t worry that their jobs are under threat quite yet!
While we might see chatbots starting to appear through the likes of Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp platforms in the coming 12 months, and will be dedicating teams of engineers to train the platforms, rather than relying on the general public. There are three main factors on which their success depends.
The first is with how much freedom AI in general is allowed to be developed, especially given the hesitation that the likes of Elon Musk and Bill Gates have about a potential ‘Singularity’, with Musk recently being quoted as saying that ‘Artificial Intelligence is our biggest existential threat’.
The second is arguably more important; how willing the general public are to help develop the chatbots, by having conversations with them, in the knowledge that they are talking to an autonomous entity.
More important still, are these chatbots going to be safe from cyberattacks? How will you know if your financial information will be secure if you disclose it to a chatbot, especially if there are unlikely to be the same multi-stage security checks that are the hallmark of P2P customer service interactions?
The Road Ahead?
Many companies are already launching bots for customer acquisition or customer service. We will see failures, and in parts, have already seen some. Bots are not trivial to build: you need people with experience in man-machine interface design. But to quote Amara’s Law: “We tend to overestimate the effect of a technology in the short run and underestimate the effect in the long run.”
Bots are here to stay, and will be a great new platform and make things easier for all of us. But bots that try to do too much or set unreasonable expectations will slow consumer confidence and acceptance of them. What might help us now is maybe to calm down a bit with the hype, and focus on building good bots that have value — then share our experiences, and show the world where the true value lies.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS
Building a Robust Data Strategy Roadmap – Part III
Add Your Heading Text Here

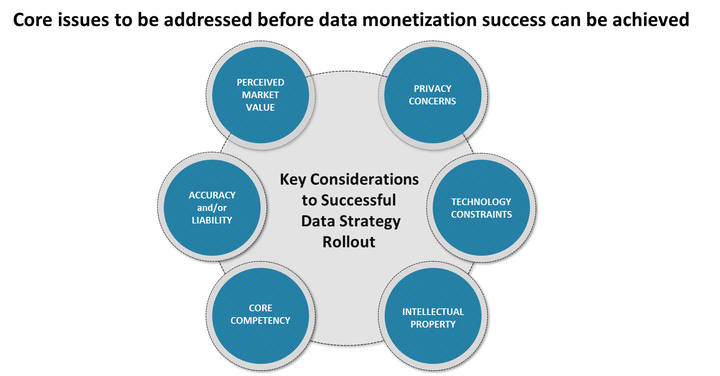
In continuation to my last article on Building a Robust Data Strategy, let me meaningfully conclude it by highlighting some of the core issues which need to be addressed before data monetization could really be called our as a success and ROI is achieved. 
Privacy Concerns
Company needs to have the implicit and/or explicit statutory or legal right, or the ethical right, to divulge private consumer data – either personalized or depersonalized, individualized or at an aggregated level. Especially in industries where regulatory bodies have a heavy clout over what data is being used to cull out actionable insights or even the data flow within or beyond the walls of the organizations. Numerous articles, reports & surveys have highlighted how crucial is for businesses to operate within the ethical boundaries of data gathering or dissemination. Leave no stone unturned to see what policies/restrictions/guidelines are in place for the industry you operate in, how easy/difficult is to access data, and what are customer or end user reactions. You definitely do not intend to burn bridges with your existing customer base or repel away new prospects. Legal actions can be fatal to business at times. Be doubly sure what you are up for!
Technology Constraints
Do have a thorough understanding of the technological or hardware-related considerations to implement the strategy chosen to monetize the data. At times, organizations don’t have the requisite resources to execute on their strategy, may be because that’s not their core area of operation or it’s happening in silo’es across the organization which the business unit in question is not privy to. A complete landscaping exercise to understand the current state of business, what’s new in the market & what the competition is up to, what’s the future state & a step-by-step roadmap to mature technological prowess. In many cases, businesses hire external consultants or seek handholding by analytics service providers who have the requisite experience in recommending about the gaps & even executing on filling those. A thorough detailed analysis (but not analysis-paralysis) is crucial to the overall success.
Intellectual Property
At times, organizations sitting on huge pile of valuable data choose to make it available in the market (as another viable revenue model to monetize data). How much data to sell and how to determine costs vs. benefits in putting valuable data on the open market should be thought through. Be privy to the pros & cons of each approach & choose your business model accordingly.
Core Competency
Depending on its core competency, organization needs to identify at which level it wants to monetize the data in the data value chain. Data at each & every touchpoint in the value chain may have its own peculiar problems (missing data, incorrect data etc) and not all of it may be relevant. If your differentiator is “speedy delivery” of goods to your customers, focus on picking the right data sets across the value chain which helps streamlining operations, optimize inventory & transit time. Know what you are best at or what you are known for in the market and harness data capabilities to strengthen your business on that front.
Data Accuracy and/or Liability
Potential problems with inaccurate or directly or indirectly regulated data insights or products hitting the market place. Make sure that data assimilation, aggregation & cleansing exercise is robust enough to ensure the analysis/insights being generated out of it have a high probability of giving the right sense of direction to the business. At times, over-ambitious expectations or poor data quality can directly impact the quality of the outcomes. Garbage-in Garbage-out is the mantra & business managers should perfectly understand the gaps in the data & be cautious before making any solid commitments.
Perceived Market Value
For larger market opportunities, it is likely that an organization would want to play at the higher level in the data value chain. Umpteen times that completely derails the whole Analytics ROI & data monetization exercise. Focus should be specifically on business model(s) used to monetize the data than otherwise.
All the aforementioned considerations should set a good pretext to the data monetization exercise and may be the key to unlocking true value from data strategy initiative. In my subsequent edition, I shall bring to light the “Analytics Centre of Excellence” concept & how can organizations setup a full-fledged Analytics unit to deliver insights to departmants/LOB’s/functions across the business and also serve as a backbone to building a data-driven organization of the future. Stay tuned !

