
Fluid supply chain transformation led by AI : A strategic PoV during COVID-19
Add Your Heading Text Here

In midst of this COVID situation across the globe, exponential technologies and an AI led processes around the value chain of supply chain will unleash new scenarios for global enterprises. Robots already stand side-by-side with their human counterparts on several manufacturing floors, adding efficiency, capacity (robots don’t need to sleep!) and dependability. Add in drones and self-driving vehicles ; all these technological advancements are compelling enterprises to reimagine their supply chain.
Supply chains, although automated to a degree, still face challenges brought about by the amount of slow, manual tasks required, and the daily management of a complex web of interdependent parts. The next generation of process efficiency gains and visibility could be on your doorstep with artificial intelligence in supply chain management, if only you’d let the robots automatically open it for you.
Intelligent Automation: Intelligent automation of the end-to-end supply chain, enabling the management of all tasks and sections in tandem allows you to spend less time on low value, high frequency activities like managing day-to-day processes, and provides more time to work on high value, exception-based requirements, which ultimately drives value for the entire business.
Analysts estimates businesses could automate up to 45% of current work, saving $2 trillion in annual wages. “In addition to the cost and efficiency advantages, Intelligent automation can take a business to the next level of productivity optimization,” . Those ‘lights out’ factories and warehouses are becoming closer to a reality.
Four key elements need to be in place for you to take full advantage of intelligent automation in your supply chain:
- robots for picking orders and moving them through the facility;
- sensors to ensure product quality and stock;
- cognitive learning systems;
- and, artificial intelligence to turn processes into algorithms to guide the entire operation.
In addition, you’ll need strong collaboration internally and among suppliers and customers to tie all management systems back to order management and enterprise resource planning platforms.
Artificial Intelligence In Supply Chain : Strategic coverage areas
AI is changing the traditional way in which companies are operating. Siemens in its “lights out” manufacturing plant, has automated some of its production lines to a point where they are run unsupervised for several weeks.
Siemens is also taking a step towards a larger goal of creating Industrie 4.0 or a fully self-organizing factory which will automate the entire supply chain. Here, the demand and order information would automatically get converted into work orders and be incorporated into the production process. This would streamline manufacturing of highly customized products.
Artificial Intelligence In Supplier Management And Customer Service: Organizations are also increasingly leveraging AI for supplier management and customer management. IPsoft’s AI platform, Amelia automates work knowledge and is able to speak to the customers in more than 20 languages. A global oil and gas company has trained Amelia to help provide prompt and more efficient ways of answering invoicing queries from its suppliers. A large US-based media services organization taught Amelia how to support first line agents in order to raise the bar for customer service.
Artificial Intelligence In Logistics & Warehousing : Logistics function will undergo a fundamental change as artificial intelligence gets deployed to handle domestic and international movement of goods. DHL has stated that its use of autonomous fork lifts is “reaching a level of maturity” in warehouse operations. The next step would be driver less autonomous vehicles undertaking goods delivery operations.
Artificial Intelligence In Procurement :AI is helping drive cost reduction and compliance agenda through procurement by generating real time visibility of the spend data. The spend data is automatically classified by AI software and is checked for compliance and any exceptions in real time. Singapore government is carrying out trials of using artificial intelligence to identify and prevent cases of procurement fraud. The AI algorithm analyzes HR and finance data, procurement requests, tender approvals, workflows, non-financial data like government employee’s family details and vendor employee to identify potentially corrupt or negligent practices. AI will also take up basic procurement activities in the near future thereby helping improve the procurement productivity.
Artificial Intelligence in new product development :AI has totally overhauled the new product development process.by reducing the time to market for new products. Instead of developing physical prototypes and testing the same, innovators are now creating 3D digital models of the product. AI facilitates interaction of the product developers in the digital space by recognizing the gestures and position of hand. For example, the act of switching on a button of a digital prototype can be accomplished by a gesture.
AI In Demand Planning And Forecasting: Getting the demand planning right is a pain point for many companies. A leading health food company leveraged analytics with machine learning capabilities to analyze their demand variations and trends during promotions. The outcome of this exercise was a reliable, detailed model highlighting expected results of the trade promotion for the sales and marketing department. Gains included a rapid 20 percent reduction in forecast error and a 30 percent reduction in lost sales.
AI in Smart Logistics :The impact of data-driven and autonomous supply chains provides an opportunity for previously unimaginable levels of optimization in manufacturing, logistics, warehousing and last mile delivery that could become a reality in less than half a decade despite high set-up costs deterring early adoption in logistics. Changing consumer behavior and the desire for personalization are behind two other top trends Batch Size One and On-demand Delivery: Set to have a big impact on logistics, on-demand delivery will enable consumers to have their purchases delivered where and when they need them by using flexible courier services.
A study by MHI and Deloitte found more than half (51%) of supply chain and logistics professionals believe robotics and automation will provide a competitive advantage. That’s up from 39% last year. While only 35% of the respondents said they’ve already adopted robotics, 74% plan to do so within the next 10 years. And that’s likely in part to keep up with key players like Amazon, who have been leading the robotics charge for the past few years.
Execution led scenario : These examples showcase that in today’s uncertain times, AI embedded supply chains offer a competitive advantage. AI armed with intelligence can analyze massive amounts of data generated by the supply chains and help organizations move to a more proactive form of supply chain management. Thus, in this AI first theme, where the mantra is “evolve or be disrupted”, companies are leveraging AI to reinvent themselves and scale their businesses quickly. AI is becoming a key enabler of the changes that businesses need to make and is helping them manage complexity of business posed by this pandemic.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

The New Code of Leadership: In midst of ambiguous, uncertain & challenging times
Add Your Heading Text Here

For Sure, 2020 will test not only the leadership acumen of CXOs, but also the ability of enterprises to operate in the face of extreme ambiguity. Starting as a localized issue, the corona virus (COVID-19) has now reached almost all nations, impacting enterprises across the globe –with dire consequences.
Already, thousands of people have died, hundreds of thousands have become ill and health services have been stressed way beyond their capacity. For most, the pandemic – and response to it – will be the most significant, and most concerning, event they have experienced. It has cost enterprises billions of dollars in lost revenue (potentially up to $2.1 trillion by the end of 2020). It is clear it will result in a significant drop in economic growth around the world. At this stage of the COVID-19 outbreak, enterprises need to deal with two equally important factors – keeping employees and their families safe, and ensuring business continuity as much as possible. Leaders are scrambling to secure supplies, keep fearful employees motivated to work, and planning for the future while dealing with the here and now. But eventually, like other Black Swan events, the virus will end. And when it does, enterprises need to be ready.
In today’s turbulent world, some have become better at planning for and mitigating against risk in the face of a crisis. They have resilience built into their structure. But for many others, this could be a time of confusion, fear, and rash decision-making. Unfortunately, in our increasingly ambiguous, volatile and inter-connected world, unanticipated events like this are likely to happen more frequently – and leaders will need to be more agile, transparent, and forward thinking. A new set of attributes will be key to navigating 2020, which is likely to be having tow strategic viewpoints . The first viewpoint will be spent dealing with safety, containment, continuity, and contingency planning – a time for prudent, agile leadership and the second viewpoint will be centered around taking advantage of the pent-up demand in the global economy through transformation and innovation.
For enterprises to respond now and plan for recovery, they must learn to operate in a state of constant disruption. In a time of unknowns, one thing is certain: what has worked in the past is unlikely to keep working in the future. New habits are forming quickly – people are working from home and consuming products and entertainment in very different ways out of necessity. Building a culture that not only tolerates this shift but thrives in it will separate the winners from the losers.
This may mean thinking differently about performance and target setting, to keep teams motivated and ensure everyone works collectively for a shared purpose – even when working remotely. It will certainly demand a proactive and empathetic communication response from leaders, who will need to consciously demonstrate the values and behaviors they wish to encourage across the organization. But it should not necessarily mean putting recruitment and retention plans on hold. In challenging times, the quality of your talent can be the ultimate advantage. Retaining your top people has never been more important, and future talent acquisition strategy will be done through the lens of recovering and resetting after the crisis. Ultimately, leaders will need to adapt quickly to changing circumstances – shifting from a measured, inclusive approach today to setting the pace post recovery and making up for lost time.
In times of crisis, people depend on leaders to provide clarity and hope. Fear can be contagious, breeding irrational behavior and anxiety – and in business, this can lead to lower productivity and employee engagement. While no one can be certain how the impact of this virus will continue to unfold globally, one thing is known: we will experience another business crisis again in the future. Leaders who can use this disruptive period as a time for self-reflection and an opportunity to re-frame their mindset are likely to be better prepared when the next crisis comes along.
This is the time for agile leaders who can anticipate change – such as the necessity of working remotely – and turn it into a positive new way of working. They can also drive a sense of collective purpose and optimism, accelerate innovation and test new ideas, partner with others, and build trust. So how can you keep responding to such volatile market demands, find new ways to create and act on opportunities, and keep your teams aligned to a common purpose? Now is the time to be in thinking different and be in action mode , a global consumer product brand has ramped up its digital outreach while foot traffic to physical stores remains low. By doubling their digital efforts, they are taking this opportunity to get closer to the customer and build a strong sense of community around their product, which in turn anticipates a significant shift in the way their products will go to market in the future.
Adaptive leaders can anticipate opportunities like this, while also using strong communication to build trust and engagement within their teams. This will set their enterprises up to thrive through recovery. Best of the leaders are known to use down cycles as opportunities to grow. The following are the five strategic interventions , leaders need to follow in this phase:
Uncertainty demands over-communication: People need reassurance that there is a plan and a path forward, If town halls and coffee chats are impossible while teams work remotely, build communication channels via WhatsApp groups or run video seminars. CEOs can share daily 90-second video updates to keep everyone aligned and build a sense of community around new tactics and plans. This gives everyone a common language to take to clients and partners. It’s even more important to stay connected with your team at this time, and create routine ways for people to work together so they feel like they’re fully supported as part of a team.
Be realistic and build no exaggeration: Leaders are now living with uncertainty and ambiguity, and it’s acceptable to say you don’t know all the answers. Listen to employee concerns, and acknowledge there are sometimes no easy solutions. If you don’t have the answer, bring your team together to discuss and experiment with solutions – focus on testing new things quickly. Being transparent and open in this way may feel uncomfortable, but it can go a long way to building credibility and trust – with staff, customers, shareholders, and the wider community.
Plan swiftly and make bold decisions: Some leaders will need to make difficult decisions in the interest of long-term business continuity – such as reducing labor costs through staff lay-offs or forced leave. Being really clear and upfront about your plan, or it could be toxic to morale. If you know there will be headcount reduction, or you need to close down a loss-making project or pull back from a market, be compassionate and clear – don’t mislead or give mixed messages, And if you have to do this, do it once and then move forward.
Engage more with your high performing teams: Leaders may need to prioritize where their energy goes – and your best talent and clients should top the list. For example, when Chinese firm provided face masks, which were already scarce, to clients very early in the outbreak, it sent a strong signal that it wanted to keep them safe. Similarly, it’s a common mistake to neglect development of high performers during economic tension – especially when you are relying on them more than ever. When the market recovers, they are likely to jump to new opportunities first. Give them the recognition they need to feel valued right now, in addition to opportunities for personal and professional development. This is one of the highest drivers of employee engagement.
Build a strong emotional intellect: Although it seems the weight of the world is on your shoulders, you still need to take time for yourself and spend time with family. Only then can you be available for your team – because working intensely under pressure for months on end is not sustainable. This includes taking time to build emotional intelligence. The four domains of Emotional Intelligence (EI) — self-awareness, self-management, social awareness, and relationship management —can help a leader face any crisis with lower levels of stress, less emotional reactivity and fewer unintended consequences, One impact of the virus is likely to be permanent change to the way organizations work. This is your opportunity to learn how to work in a more agile way, including virtual working and rapid prototyping.
This is a critical moment to develop the leadership capabilities you will need for a very different future. Are you ready for the challenge?
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS
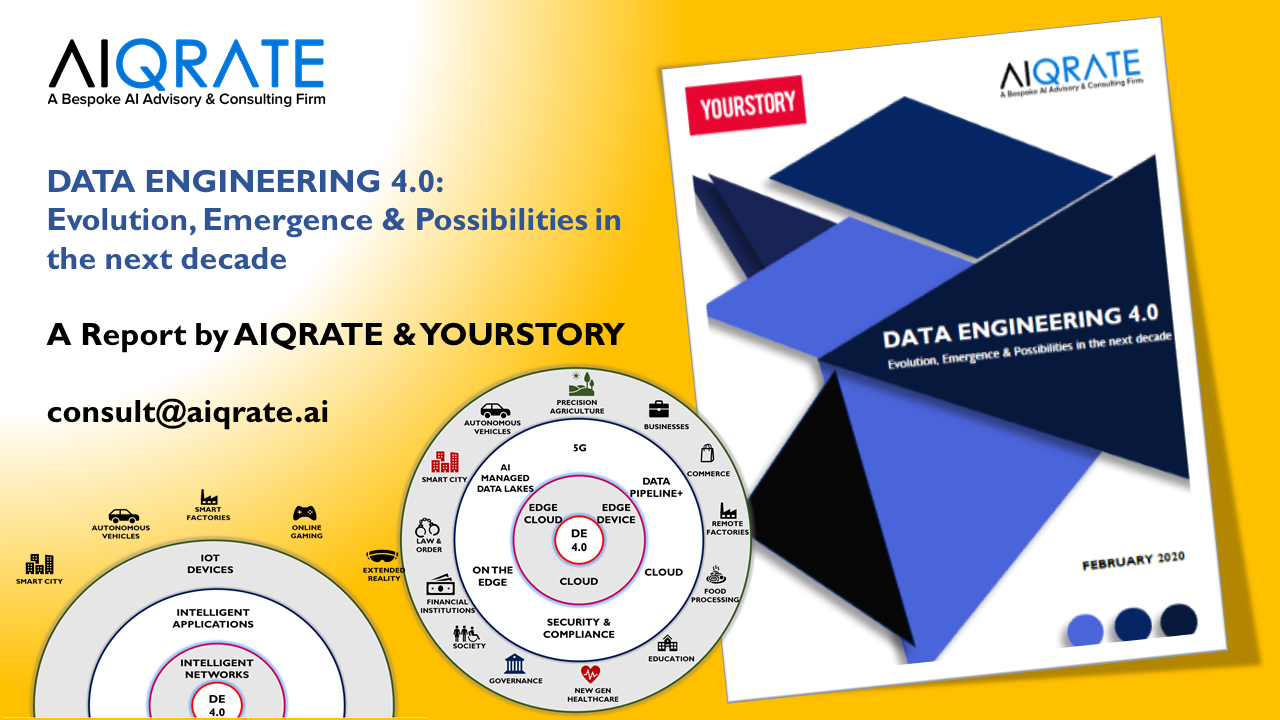
REPORT: Data Engineering 4.0: Evolution, Emergence and Possibilities in the next decade
Add Your Heading Text Here

Today, most technology aficionados think of data engineering as the capabilities associated with traditional data preparation and data integration including data cleansing, data normalization and standardization, data quality, data enrichment, metadata management and data governance. But that definition of data engineering is insufficient to derive and drive new sources of society, business and operational value. The Field of Data Engineering brings together data management (data cleansing, quality, integration, enrichment, governance) and data science (machine learning, deep learning, data lakes, cloud) functions and includes standards, systems design and architectures.
There are two critical economic-based principles that will underpin the field of Data Engineering:
Principle #1: Curated data never depletes, never wears out and can be used an unlimited number of use cases at a near zero marginal cost.
Principle #2: Data assets appreciate, not depreciate, in value the more that they are used; that is, the more these data assets are used, the more accurate, more reliable, more efficient and safer they become.
There have been significant exponential technology advancements in the past few years ; data engineering is the most topical of them. Burgeoning data velocity , data trajectory , data insertion , data mediation & wrangling , data lakes & cloud security & infrastructure have revolutionized the data engineering stream. Data engineering has reinvented itself from being passive data aggregation tools from BI/DW arena to critical to business function. As unprecedented advancements are slated to occur in the next few years, there is a need for additional focus on data engineering. The foundations of AI acceleration is underpinned by robust data engineering capabilities.
YourStory & AIQRATE curated and unveiled a seminal report on “Data Engineering 4.0: Evolution , Emergence & Possibilities in the next decade.” A first in the area , the report covers a broad spectrum on key drivers of growth for Data Engineering 4.0 and highlights the incremental impact of data engineering in the time to come due to emergence of 5G , Quantum Computing & Cloud Infrastructure. The report also covers a comprehensive section on applications across industry segments of smart cities , autonomous vehicles , smart factories and the ensuing adoption of data engineering capabilities in these segments. Further , it dwells on the significance of incubating data engineering capabilities for deep tech startups for gaining competitive edge and enumerates salient examples of data driven companies in India that are leveraging data engineering prowess . The report also touches upon the data legislation and privacy aspects by proposing certain regulations and suggesting revised ones to ensure end to end protection of individual rights , security & safety of the ecosystem. Data Engineering 4.0 will be an overall trojan horse in the exponential technology landscape and much of the adoption acceleration that AI needs to drive ; will be dependent on the advancements in data engineering area.
Please fill in the below details to download the complete report.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Survival of the Fittest : AI will be the secret sauce to stay relevant
Add Your Heading Text Here

In the time of uncertainty and disruption….Soon, organizations will increasingly be competing on the AI prowess and their supremacy. AI promises to play a critical role ; artificial intelligence can detect patterns in complex data sets at extreme speed and scale, enabling dynamic learning. This will allow organizations to constantly adapt to changing realities and surface new opportunities, which will be increasingly important in an uncertain and fast-changing environment.
But for companies to compete on AI, it is not enough to merely adopt AI, which alone can accelerate learning only in individual activities. As with previous transformative technologies, unlocking the full potential of AI and future of workforce will require fundamental organizational innovation , transformation and disruption. Leaders will need to re-invent the enterprise as an AI driven organization :
- Velocity & Scale : The growing opportunity and need to perform at high velocity bringing scale driven by AI is well known—algorithmic trading, dynamic pricing, real-time customized product recommendations are already a reality in many businesses. But it is perhaps under-appreciated that slow moving forces are also becoming important. For example, trade institutions, political structures and social attitudes are slowly changing in ways that could have a profound impact on business. Gone are the days when business leaders could focus only on business and treat these broader variables as constants or stable trends. But such shifts unfold over many years or even decades. In order to thrive sustainably, businesses must learn at high velocity .
- Rebalancing Humans and Machines equation : Machines have been crucial components of businesses for centuries—but in the AI age, they will likely expand rapidly into what has traditionally been considered white-collar work. Instead of merely executing human-directed and designed processes, machines will be able to learn and adapt, and will therefore have a greatly expanded role in future organizations. Humans will still be indispensable, but their duties will be quite different when complemented or substituted by intelligent machines.
- Integrating External ecosystems with corporate strategies : Businesses are increasingly acting in multi company ecosystems that incorporate a wide variety of players. Indeed, seven of the world’s largest companies, and many of the most profitable ones, are now platform businesses. Ecosystems greatly expand learning potential: they provide access to exponentially more data, they enable rapid experimentation, and they connect with larger networks of suppliers of customers. Harnessing this potential requires redrawing the boundaries of the enterprise and effectively influencing economic activity beyond the orchestrating company.
- Evolving the Organization : The need for dynamic learning does not apply just to customer-facing functions—it also extends to the inner workings of the enterprise. To take advantage of new information and to compete in dynamic, uncertain environments, the organizational context itself needs to be evolve in the face of changing external conditions.
Today’s organizations, which were designed for more stable business environments, are not well-suited to perform these functions. Reinventing the organization for the next decade will require embracing four imperatives:
- Integrate AI into the core operating model for survival
- Migrate human cognition to mature work spheres
- Re balance the relationship between machines and humans.
- New age leadership & management approaches
1.Integrate AI into the core operating model for survival : As powerful as today’s level of AI is , it will yield only incremental gains if it simply enhance individual steps of existing processes. The effective rate of an organization’s learning is gated by its ability to act on new insights. And classical organizations act slowly, owing to their reliance on human decision making and hierarchy. Organizations will need not only to automate but also to “embed AI in to the operating model” of significant parts of their businesses.
In order to truly accelerate the speed of learning to algorithmic timescales, organizations will need not only to automate but also to “embed AI ” into significant parts of their businesses. In traditional automation, machines execute a pre-designed process repeatedly and consistently. In AI led transformation, machines use continuous feedback to act, learn, and adapt on their own—without the bottleneck of human intervention.
AI driven systems are designed by combining multiple algorithms into integrated learning loops. Data from digital platforms automatically flows into AI algorithms, which mine the information in real time to facilitate new insights and decisions. These are wired directly into action systems, which continuously optimize outcomes under changing conditions. These actions produce yet more data that can be fed back through the cycle, closing the loop and allowing the organization to learn at the speed of algorithms.
In contrast, traditional organizational approaches—for example, unchanging rules or hierarchical decision processes—can impede companies’ ability to harness the rapid learning potential unlocked by AI ; Actions that companies can take to harness AI include :
- Gather real-time data on all aspects of the business by leveraging algorithms
- Deploy AI at scale, integrated with data and decision-making systems.
- Take human hierarchy “out of the loop” of routine, data-based decision making.
2. Migrate Human Cognition to Mature Work Spheres :The widespread adoption of AI naturally raises the question of what role human workers will play in the organization of the future. Today, there is already widespread concern about the speed at which AI will disrupt the future of work. To shape this future—and to maximize organizational learning capabilities—businesses need to focus human cognition on its unique strengths. Humans should increasingly focus their efforts on these higher-level activities. For example, while correlative analysis is generally sufficient for learning about repeated actions on fast timescales, it is less useful for learning about slow-moving forces, such as political, social, and economic trends. These shifts are unique and depend on the historical context and trajectory, which means there is no repeated data set in which to find patterns. Human abilities, such as understanding causal relationships and generalizing from limited data, are necessary to decode these forces and adapt the organization accordingly.
Counterfactual thinking is also critical, as businesses need increasingly to compete on Imagination. Existing business models are being exhausted faster, and long-term growth is declining, which means companies must continually generate new ideas to grow sustainable. But businesses today, which are often implicitly designed for efficiency and the maximization of short run financial outcomes, are not conducive to imagination. Organizations will need to better facilitate individual and collective imagination.
In addition to imagination and making sense of non-repeated events, there will be many other activities where humans are advantaged, including organizational design, algorithmic governance, ethics, and purpose, to name a few. In these domains of human activity, organizations will need to become more effective at dynamic collaboration to get the most out of their teams. This requires emphasizing self-organization and experimentation by creating an organizational context in which responsive decision making and learning can thrive, rather than by relying on direct instructions.
3. Rebalance the Relationship Between Humans and Machines : The first two imperatives call for a hybrid organization, one that combines the comparative advantages of machines and humans: machines’ ability to rapidly identify complex patterns in big data and humans’ ability to decode complex causal relationships and imagine new possibilities. Together, these will enable the organization to learn on an expanded range of timescales—faster and slower.
But in hybrid organizations, humans and machines will increasingly have to collaborate in new and more effective ways. This includes tasks that require thinking on multiple levels or timescales simultaneously, as well as tasks that demand social interaction, another dimension in which humans are currently far more effective. Organizations will thus need to reimagine the relationship between humans and machines to bring the best out of both and maximize synergies.
Today’s AI models tend to be “black boxes” that are not designed to be interoperable and may therefore impede trust. For these new types of human-machine relationships to succeed, organizations need to develop effective human-machine interfaces that allow for seamless collaboration. Organizations will need to overcome these hurdles by developing and implementing interfaces that provide transparency into how AI makes recommendations, allowing humans to understand and validate machines’ actions. Similarly, humans and algorithms are rarely matched for bandwidth and complexity. Choosing the right level of abstraction and compression for communication between humans and computers is critical: too much compression will suppress subtlety and prevent the tinkering through which human innovation proceeds, while too little will overwhelm human overseers.
4. New Age Leadership & Management Approaches :Collectively, the above imperatives point to a very different way of designing and operating organizations with AI —which in turn will significantly change the role of leadership. In particular, leaders will need to focus on several new challenges.Developing governance principles for AI and autonomous machines. : As machines play a greater part in learning and action, the role of leadership in setting guardrails and priorities will take on greater importance. In the last decade, tech companies could sidestep these topics, as the promise and potential of new technologies gave them a license to move fast. But as social scrutiny of technology increases, questions about governance, trust, and ethics are coming to the forefront. And as AI is adopted more widely, all businesses will have to deal with these difficult questions.
The organizations that will survive and become pioneer will look much different from today’s: they will use different AI driven capabilities; they will operate at different speeds and scales of influence; they will contain different structures and responsibilities; and they will embody different leadership models to enable all of the above. AI will become a force multiplier and will define the DNA of tomorrow’s organization.At the end of the day, its a matter of survival….
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Key Strategic Imperatives for GCCs to drive AI Center of Excellence : The new model
Add Your Heading Text Here

Global Capability Centers(GCC’s) are at an inflection point as the pace at which AI is changing every aspect is exponential and at high velocity. The rapid transformation and innovation of GCC’s today is driven largely by ability for them to position AI strategic imperative for their parent organizations. AI is seen to the Trojan horse to catapult GCC’s to the next level on innovation & transformation. In recent times; GCC story is in a changing era of value and transformative arbitrage. Most of the GCCs are aiming towards deploying suite of AI led strategies to position themselves up as the model template of AI center of Excellence . It is widely predicted that AI will disrupt and transform capability centers in the coming decades. How are Global Capability Centers in India looking at positioning themselves as model template for developing AI center of competence? How have the strategies of GCCs transformed with reference to parent organization? whilst delivering tangible business outcomes , innovation & transformation for parent organizations?
Strategic imperatives for GCC’s to consider to move incrementally in the value chain & become premier AI center of excellence
AI transformation
Artificial Intelligence has become the main focus areas for GCCs in India. The increasing digital penetration in GCCs across business verticals has made it imperative to focus on AI. Hence, GCCs are upping their innovation agenda by building bespoke AI CoEs. Accelerated AI adoption has transcended industry verticals, with organizations exploring different use cases and application areas. GCCs in India are strategically leveraging one of the following approaches to drive the AI penetration ahead –
- Federated Approach: Different teams within GCCs drive AI initiatives
- Centralized Approach: Focus is to build a central team with top talent and niche skills that would cater to the parent organization requirements
- Partner ecosystem : Paves a new channel for GCCs by partnering with research institutes , start-ups , accelerators
- Hybrid Approach: A mix of any two or more above mentioned approaches, and can be leveraged according to GCC’s needs and constraints.
Ecosystem creation : Startups /research institutes/Accelerators
One of the crucial ways that GCCs can boost their innovation agenda is by collaborating with start-ups, research institutes , accelerators. Hence, GCCs are employing a variety of strategies to build the ecosystem. These collaborations are a combination of build, buy, and partner models:
- Platform Evangelization: GCCs offer access to their AI platforms to start-ups
- License or Vendor Agreement: GCCs and start-ups enter into a license agreement to create solutions
- Co-innovate: Start-ups and GCCs collaborate to co-create new solutions & capabilities
- Acqui-hire: GCCs acquire start-ups for the talent & capability
- Research centers : GCCs collaborate with academic institutes for joint IP creation , open research , customized programs
- Joint Accelerator program : GCCs & Accelerators build joint program for customized startups cohort
To drive these ecosystem creation models, GCCs can leverage different approaches. Further, successful collaboration programs have a high degree of customization, with clearly defined objectives and talent allocation to drive tangible and impact driven business outcomes.
AI Center of Competence/ Capability
GCCs are increasingly shifting to competency , capability creation models to reduce time-to-market. In this model, the AI Center of Competence teams are aligned to capability lines of businesses where AI center of competence are responsible for creating AI capabilities , roadmaps and new value offerings, in collaboration with parent organization’s business teams. This alignment and specific roles have clear visibility of the business user requirement. Further, capability creation combined with parent organization’s alignment helps in tangible value outcomes. In several cases, AI teams are building new range of innovation around AI based capabilities and solutions to showcase ensuing GCC as model template for innovation & transformation . GCCs need to conceptualize a bespoke strategy for building and sustaining AI Center of Competence and keep it up on the value chain with mature and measured transformation & innovation led matrices.
Talent Mapping Strategy
With the evolution of analytics ,data sciences to AI , the lines between different skills are blurring. GCCs are witnessing a convergence of skills required across verticals. The strategic shift of GCCs towards AI center of capability model has led to the creation of AI , data engineering & design roles. To build skills in AI & data engineering, GCCs are adopting a hybrid approach. The skill development roadmap for AI is a combination of build and buy strategies. The decision to acquire talent from the ecosystem or internally build capabilities is a function of three parameters –Maturity of GCC ’s existing AI capabilities in the desired or adjacent areas ,Tactical nature of skill requirement & Availability and accessibility of talent in the ecosystem. There’s always a heavy Inclination towards building skills in-house within GCCs and a majority of GCCs have stressed upon that the bulk of the future deployment in AI areas will be through in-house skill-building and reskilling initiatives. However, talent mapping strategy for building AI capability is a measured approach else can result in being a Achilles heel for GCC and HR leaders.
GCCs in India are uniquely positioned to drive the next wave of growth with building high impact AI center of competence , there are slew of innovative & transformative models that they are working upon to up the ante and trigger new customer experience , products & services and unleash business transformation for the parent organizations. This will not only set the existing GCCs on the path to cutting-edge innovation but also pave the way for other global organizations contemplating global center setup in India.AI is becoming front runner to drive innovation & transformation for GCCs.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Future of Work 2020: Sameer Dhanrajani, Co-founder of AIQRATE, shares his take on the power of AI
Add Your Heading Text Here

Will artificial intelligence (AI) take over human intelligence? Is AI applicable across every industry? What is the cost of implementing AI, is it expensive? Is AI complex? AI is not for the masses?
There is hardly any industrial domain today which is not harnessing the benefits of artificial intelligence to accomplish efficiency, accuracy, and affordability, while cutting down on the time taken by manual processes. And yet, there are a million myths surrounding this re-merging tech tool that continues to question the utility and implementation of AI in day-to-day activities.
Sameer Dhanrajani, Chief Executive Officer and Co-founder, AIQRATE Advisory & Consulting, busted some of these myths on Day 1 of Future of Work, India’s largest product-tech-design conference hosted by YourStory.
To explain his point further, he cited the example of Japan’s Makoto Koike. An engineer by education, Makoto went back to his parent’s cucumber farm and began developing a new approach with the help of technology. In the process, Makoto realised there was something in the making – the making of an algorithm, which could give him some understanding about the yield, crop, and the prices. And this is just one area of the application of AI.
According to Sameer, there are at least three strategic imperatives for growth through AI and it involves re-imagining customer experiences, innovating new products and services, and transforming businesses. The AI advisor also touched upon the algorithm economy, explaining how algorithms are impacting modern decision making.
From healthcare to education, sanitation, and marketing practices, artificial intelligence is making its presence felt across sectors today. While AI alone might not be able to address all issues and solve all the problems, Sameer notes that combined with data intelligence and design, it can surely revolutionise the future.
Read more at: https://yourstory.com/2020/02/future-of-work-sameer-dhanrajani-artificial-intelligence
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Experience the Algorithm Economy : Accentuating strategic value for the enterprises
Add Your Heading Text Here

Algorithms will not only drive scores of business processes, but also build other self-intuitive algorithms, much as robots can build other robots. And rather than using apps, future users’ lives will revolve personalized algorithms to drive individual choices and behaviors .
Enterprises will license, trade, sell and even give away non-lynch pin algorithms and single-function software snippets that provide new opportunities for innovation by other enterprises. Enterprises will also partner with cloud-based, automated suppliers with the industry expertise to advice on ways to avoid future risk and adapt to technology trends.
Imaginative thinking ! but it’s no surprise that future value will come from increased density of interactions, relationships and sharing between people, businesses and things ̶ or what I call “ Algorithm Economy “ .The greater the maturity of algorithms , the greater potential value you can reap. We’ve seen interconnection coming of age for a while now and have invested heavily in a platform to empower enterprises with fast, direct and secure interconnections with business partners and network and cloud service providers.
Redefining Business Architecture with Algorithms
The term “algorithm economy” is relatively new, but the practical use of algorithms is already well established in many industries. In my opinion , CXOs must begin designing their algorithmic business models, both to capitalize on their potential for business differentiation, and to mitigate the possible risks involved.
Established businesses need to adopt a “bi modal strategy” and build what I called an algorithmic platform, completely separate from legacy systems, that harnesses repository of algorithms, interconnections, the cloud and the Internet of Things (IoT) to innovate, share value, increase revenues and manage risk.
New platforms based on this bimodal model should be far simpler, more cloud-based and more flexible than in the past, with the ability to add and remove capabilities “like Velcro” to support new short- and long-term projects. At the same time, IT should start divesting itself of older systems and functions that are outliving their usefulness or could be better done by other methods. The significant development and growth of smart machines is a major factor in the way algorithms have emerged from the shadows, and become more easily accessible to every organization. We can already see their impact in today’s world, but there is much work ahead to harness the opportunities and manage the challenges of algorithmic business.
CXOs should examine how algorithms and intelligent machines are already used by competitors and even other enterprises to determine if there is relevance to their own needs. The retail sector has long been at the leading edge of using smart algorithms to improve business outcomes. Today, many retail analysts believe that the algorithms that automate pricing and merchandising may soon become the most valuable asset that a retailer can possess. In HR function, algorithms are already transforming talent acquisition as they are able to rapidly evaluate the suitability of candidates for specific roles, but the same technology could easily be applied within an enterprise to allocate workloads to the right talent. In healthcare, the open availability of advanced clinical algorithms is transforming the efficiency of healthcare delivery organizations and their ability to deliver care. The practice of sharing and co-developing algorithms between enterprises with mutual interests could be relevant to most enterprises.
The Challenges of Algorithm Economy
The advances and benefits of algorithm economy will come hand in hand with obstacles to navigate. Whether the problems are anticipated or unexpected, as quantum computing becomes more pervasive, the implications have the potential to make or break organizations. For example, an extreme point of view is that any beneficial effects of algorithms on humanity may be nullified by algorithmically driven systems that are antithetical to human interests. Or, while an algorithmic business model may be deployed with good intentions, it could be manipulated by malicious humans to achieve undesirable outcomes. Undesirable, at least, from the point of the view of the person or organization that owns or controls the algorithm. Algorithms rely on the data they are fed, and their decisions are only as good as the data they are based on. Moreover, tricky ethical problems that do not necessarily have a “correct” answer will be inevitable, as a greater complexity of decision making is left in the hands of automated systems.
The scale of change that is made possible by smart machines and algorithm economy warrants considerable planning and testing. Enterprises that fail to prepare risk being left behind or facing unexpected outcomes with negative implications.
The Transformation required in Algorithm Economy
Making sense of all the data about how customers behave, and what connected things tell an organization, will require algorithms to define business processes and create a differentiated customer experience. Algorithms will evaluate suppliers, define how our cars operate, and even determine the right mix of drugs for a patient. In the purely digital world, agents will act independently based on our algorithms, in the cloud. In the 2020s, we’ll move away from using apps to rely on virtual assistants – basically, algorithms in the cloud – to guide us through our daily tasks. People will trust personal algorithms that thinks and acts for them. Take this to another level and the algorithms themselves will eventually become smart by learning from experience and producing results their creators never expected.
The Final Frontier
Therefore, we have to get the architecture of algorithms robust and steady to derive meaningful objectives. In essence, algorithms spot the business moments, meaningful connections, and predict ill behaviors and threats. CXOs need to be the strategic voice on the use of information, to build the right set of intelligent insights. Experience the Algorithm Economy and the ensuing strategic value for your enterprise . Are you geared up ?
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

How AI is shaping the new life in life sciences and pharmaceutical industry
Add Your Heading Text Here

The pharma and life sciences industry is faced with increasing regulatory oversight, decreasing R&D productivity, challenges to growth and profitability, and the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) in the value chain. The regulatory changes led by the far-reaching Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) in the US are forcing the pharma and life sciences industry to change its status quo.
Besides the increasing cost of regulatory compliance, the industry is facing rising R&D costs, even though the health outcomes are deteriorating and new epidemics are emerging. Led by the regulatory changes, the customer demographics are also changing. The growth is being driven by emerging geographies of APAC and Latin American region.
Disruption in life sciences
Pharmaceutical organisations can leverage AI in a big way to drive insightful decisions on all aspects of their business, from product planning, design to manufacturing and clinical trials to enhance collaboration in the ecosystem, information sharing, process efficiency, cost optimisation, and to drive competitive advantage.
AI enables data mining, engineering, and real time- and algorithmic-driven decision-making solutions, which help in responding to the following key business value chain disruptions in the pharmaceutical industry:
- AI-driven drug discovery – Enables scientists to source scientific findings and insights from external labs or internal knowledge to jump start discovery which will in turn help reduce cycle time for product development aiding faster go-to-market
- Reduce cycle times for clinical trials– Through better insights driven by improved accuracy of machine-based ensemble algorithms
- Supply chain transformation – Building predictive algorithms using a combination of internal and external data would help reduce unforeseen shortages in availability of drugs impacting customer service levels and lost sales revenues
- Product failure prediction – Via root cause analysis and predictive algorithms of product failures (vendor data)
- Risk management – For evaluation of potential risks posed by elemental impurities in a formulated drug product
- Real-time medical device analysis and visualisation– Leveraging interconnecting data from implanted devices and personal care devices
- Behavioural sciences – To more fully understand customer perceptions about their products which helps in proactively fixing product issues or managing communication better
- Enhance reporting systems– To meet the changing regulatory compliance needs more effectively
- Intelligent insights – Renew focus on understanding the underlying business data and generating insights using latest insights and intelligence frameworks
The human microbiome
Though genomics currently hogs the spotlight, there are plenty of other biotechnology fields wrestling with AI. In fact, when it comes to human microbes – the bacteria, fungi, and viruses that live on or inside us – we are talking about astronomical amounts of data. Scientists with the NIH’s Human Microbiome Project have counted more than 100 trillion microbes in the human body.
- Cambridge Semantics has a developed semantic web technologies that help pharmaceutical companies sort and select which businesses to acquire and which drug compounds to license.
- Data scientists at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have developed the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV), open source software that allows for the interactive exploration of large, integrated genomic datasets.
- GNS Healthcare is using proprietary causal Bayesian network modeling and simulation software to analyse diverse sets of data and create predictive models and biomarker signatures.
Genomics
- Sequencing millions of human genomes would add up to hundreds of petabytes of data.
- Analysis of gene interactions multiplies this data even further.
In addition to sequencing, massive amounts of information on structure/function annotations, disease correlations, population variations – the list goes on – are being entered into databanks. Software companies are furiously developing tools and products to analyse this treasure trove.
Robust algorithms with massive data engineering capabilities
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

How the insurance industry can leverage AI to enhance efficiencies
Add Your Heading Text Here

This second machine age has seen the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), or intelligence that is not the result of human cogitation. AI is now ubiquitous in many commercial products, from search engines to virtual assistants.
The massive amounts and the speed at which structured and unstructured (e.g., text, audio, video, sensor) data is being generated has made speedy processing and generation of meaningful, actionable insights imperative.
The insurance industry segment has been conservative in adopting AI across the value chain, but P&C /Life/Reinsurance companies have accelerated the pace of AI adoption and initiated deployment of AI use cases across the value chain.
Here are few of the use cases leveraging AI for the insurance industry:
Personalised customer experience: redefining the value proposition
Many insurers are already in the early stages of enhancing and personalising the customer experience. Exploiting social data to understand customer needs and sentiments about products and processes (e.g., claims) are some early applications of AI.
The next stage in robo-advisor evolution is to offer better intelligence on customer needs and goal-based planning for both protection and financial products. Recommender systems and “someone like you” statistical matching will become increasingly available to customers and advisors.
Up next will be understanding of individual and household balance sheets and income statements, as well as economic, market, and individual scenarios to recommend, monitor and alter financial goals and portfolios for customers and advisors.
Automated and augmented underwriting: enhancing efficiencies
This involves automating large classes of standardised underwriting in auto, home, commercial (small and medium business), life, and group using sensor (IoT) data, unstructured text data (e.g., agent/advisor or physician notes), call centre voice data, and image data using Bayesian learning or deep learning techniques.
The industry will also model new business and underwriting process using soft robotics and simulation modeling to understand risk drivers and expand the classes of automated and augmented (i.e., human-performed) underwriting.
We will also see augmenting of large commercial underwriting and life/disability underwriting by having AI systems (based on NLP and DeepQA) highlight key considerations for human decision-makers. Personalised underwriting by a company or individual takes into account unique behaviours and circumstances.
Robo-claims adjuster
This will help build predictive models for expense management, high value losses, reserving, settlement, litigation, and fraudulent claims using existing historical data. It will also help analyse claims process flows to identify bottlenecks and streamline flow, leading to higher company and customer satisfaction.
Building a robo-claims adjuster by leveraging predictive models and building deep learning models that can analyze images to estimate repair costs can change status quo. In addition, use of sensors and IoT to proactively monitor and prevent events can reduce losses.
A claims insights platform that can accurately model and update frequency and severity of losses over different economic and insurance cycles (i.e., soft vs. hard markets) can help the industry. Carriers can apply claims insights to product design, distribution, and marketing to improve overall lifetime profitability of customers.
Emerging risks and new product innovation
Identifying emerging risks (e.g., cyber, climate, nanotechnology), analyse observable trends, determining if there is an appropriate insurance market for these risks, and developing new coverage products in response historically have been creative human endeavors.
Man and machine learning
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) that can perform any task that a human can is still a long way off. In the meantime, combining human creativity with mechanical analysis and synthesis of large volumes of data – in other words, man-machine learning (MML) – can yield immediate results.
For example, in MML, the machine learning component sifts through daily news from a variety of sources to identify trends and potentially significant signals. The human learning component provides reinforcement and feedback to the ML component, which then refines its sources and weights to offer broader and deeper content.
Using this type of MML, risk experts (also using ML) can identify emerging risks and monitor their significance and growth. MML can further help insurers to identify potential customers, understand key features, tailor offers, and incorporate feedback to refine new product introduction.
AI implications for insurers
Improving Efficiencies: AI is already improving efficiencies in customer interaction and conversion ratios, reducing quote-to-bind and FNOL-to-claim resolution times, and increasing new product speed-to market. These efficiencies are the result of AI techniques speeding up decision-making (e.g., automating underwriting, auto-adjudicating claims, automating financial advice, etc.).
Improving effectiveness: Because of the increasing sophistication of its decision-making capabilities, AI soon will improve target prospects to convert them to customers, refine risk assessment and risk-based pricing, enhance claims adjustment, and more. Over time, as AI systems learn from their interactions with the environment and with their human masters, they are likely to become more effective than humans and replace them. Advisors, underwriters, call centre representatives, and claims adjusters likely will be most at risk.
Improving risk selection and assessment: AI’s most profound impact could well result from its ability to identify trends and emerging risks, and assess risks for individuals, corporations, and lines of business. Its ability to help carriers develop new sources of revenue from risk and non-risk based information will also be significant.
Read more at: https://yourstory.com/2020/02/insurance-industry-leverage-ai-enhance-efficiencies
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

AI for Startups: 4 adoption recommendations entrepreneurs should keep in mind
Add Your Heading Text Here

Despite nationwide venture funding hitting a multiyear low, venture capital deployed to artificial intelligence (AI) startups has reached a record high.
Last year, VCs struck 859 deals with AI companies, nearly five times the number that signed on the dotted line four years earlier. To date, the market has 2,045 AI startups and more than 17,000 market followers, with more joining by the day.
AI’s rapid rise has swept up startups and enterprises alike, including US automaker Ford, which recently bought AI startup Argo for $1 billion. The acquisition cements experts’ suspicions of Ford’s coming foray into self-driving technology. Other startups — so many, in fact, that entrepreneurs need a “best of” guide — are betting heavily on bot platforms.
Sixty-eight percent of marketing executives report using AI in their function. For a practice that only went mainstream in 2016 and barely existed four years ago, that’s a remarkable adoption rate.
How, regardless of the platform you choose, can you join forward-thinking entrepreneurs and build your business with AI? Over the last few years, I have worked closely with multiple startups across genres and ,So far, four strategic considerations stand out to leverage AI in your startups:
1. Get to know your next customer
A politician wouldn’t dream of delivering a small-town stump speech to urban constituents. Why? Because you’ve got to know your audience. The same is true for entrepreneurs. Before you broadcast your message, you need to know who you’re trying to reach.
Node, an account-based intelligence startup, uses natural language processing — a fancy term for teaching a computer to understand how we humans speak and write — to develop customer profiles. Node is crunching vast swaths of data to connect the dots between marketers and companies they’re trying to reach.
Once you have ample customer data — Node uses data crawlers to scrape information from social media, news sites, and more — pair machine learning and natural language processing models to extract sentiments from unstructured data. Then, just as senators segment constituents into demographic groups, Node uses cluster analysis to sort clients’ customers into like cohorts.
2. See how people truly use your product
If, heaven forbid, you forgot to tag your neighbour at last week’s house party, Facebook was no doubt there to remind you of your error. How does Facebook know which of your friends you left untagged? It has gone all-in on an AI technique called convolutional neural networks.
Convolutional neural networks, which loosely model how the brain’s visual cortex interacts with the eyes, work by separating an image into tiny portions before running each of those specks through a multilayered filter. It then “sees” where each speck overlaps with other parts of the image, and through automated iterations, puts together a full image.
Many different ways exist to apply this technology, but retail businesses can start with image classification. Try using a convolutional neural network to break down photos of your products posted online. The model can identify customer segments that frequently use your product, where they’re using it and whether they commonly pair other products with yours. Essentially, this automated image analysis can show you how your products fit into customers’ lives, allowing you to tailor your marketing materials to fit.
3. Get inside the user’s experience
Fortunately, AI can take the emotional temperature of thousands of customers at once. Dumbstruck, a video-testing and analytics startup that I advise, has added natural language processing to its emotional analytics stack. This allows it to provide moment-by-moment insights into viewers’ reactions to media. Dumbstruck’s model grows stronger with each reaction analysed, producing a program that perceives human emotions even better than some people can.
4. Provide affordable, always-on support
Customer service is — or should be, according to consumers — the department that never sleeps. More than half of people, 50.6 percent to be precise, believe a business should be available 24/7 to answer their every question and concern. When asked whether businesses should be available via a messaging app, the “yes” votes jump to nearly two in three. Fortunately, bots don’t sleep, eat or go off-script.
A well-built bot can offer cost-effective, constant customer service. Of course, grooming your bot to serve customers requires front-end data — ideally hundreds of thousands of example conversations — but you can get started with a human-chatbot hybrid. With this approach, the bot answers run-of-the-mill questions, while a human takes over for the more complex ones. Then, as data builds and the model matures, you can phase in full automation.
AI’s impact on startups
Startups will gain a competitive edge in capturing the AI market. Larger enterprises will provide the infrastructure to startups for building innovative services. It is somewhat similar to the business model followed when cable technology was introduced.
Startups leveraging AI technology for industry verticals, including agriculture, manufacturing or insurance, are bound to be successful.
Startups can empower established insurance companies like State Farm, Allstate, and Farmers with technology, enabling them to become more proactive in policy planning. For instance, a new AI insurance underwriter will help to forecast natural disasters and accidents, and adjust premiums.
The predictive, decision-making capabilities are more than just a novel technology. You can manage food supply chains with the help of AI. Startups could develop end-to-end farming solutions with AI analytics for reducing food waste. It will have a huge impact in tackling global issues of hunger and famine.
AI will be a fundamental predictive enabler helping us solve large-scale problems, and startups are poised to gain a competitive edge.
Ground-level AI sentiment of startups Regardless of which industry you operate, AI will affect your world in some way. Look into what is present now and how you can use it to gain a competitive edge. The possibilities with AI are endless; enterprises will become efficient, intelligent, and cost-effective. Undoubtedly, the AI revolution will advance to a point where it will offer real-world benefits to every business, large and small.

