
The ‘Dark’ side of AI: Algorithm Bias, influenced decision making.. Defining AI Ethics Strategy
Add Your Heading Text Here

According to a 2019 report from the Centre for the Governance of AI at the University of Oxford, 82% of Americans believe that robots and AI should be carefully managed. Concerns cited ranged from how AI is used in surveillance and in spreading fake content online (known as deep fakes when they include doctored video images and audio generated with help from AI) to cyber attacks, infringements on data privacy, hiring bias, autonomous vehicles, and drones that don’t require a human controller.
What happens when injustices are propagated not by individuals or organizations but by a collection of machines? Lately, there’s been increased attention on the downsides of artificial intelligence and the harms it may produce in our society, from unequitable access to opportunities to the escalation of polarization in our communities. Not surprisingly, there’s been a corresponding rise in discussion around how to regulate AI.
AI has already shown itself very publicly to be capable of bad biases — which can lead to unfair decisions based on attributes that are protected by law. There can be bias in the data inputs, which can be poorly selected, outdated, or skewed in ways that embody our own historical societal prejudices. Most deployed AI systems do not yet embed methods to put data sets to a fairness test or otherwise compensate for problems in the raw material.
There also can be bias in the algorithms themselves and in what features they deem important (or not). For example, companies may vary their product prices based on information about shopping behaviors. If this information ends up being directly correlated to gender or race, then AI is making decisions that could result in a PR nightmare, not to mention legal trouble. As these AI systems scale in use, they amplify any unfairness in them. The decisions these systems output, and which people then comply with, can eventually propagate to the point that biases become global truth.
The unrest on bringing AI Ethics
Of course, individual companies are also weighing in on what kinds of ethical frameworks they will operate under. Microsoft president Brad Smith has written about the need for public regulation and corporate responsibility around facial recognition technology. Google established an AI ethics advisory council board. Earlier this year, Amazon started a collaboration with the National Science While we have yet to reach certain conclusions around tech regulations, the last three years have seen a sharp increase in forums and channels to discuss governance. In the U.S., the Obama administration issued a report in 2016 on preparing for the future of artificial intelligence after holding public workshops examining AI, law, and governance; AI technology, safety, and control; and even the social and economic impacts of AI. The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), an engineering, computing, and technology professional organization that establishes standards for maximizing the reliability of products, put together a crowdsourced global treatise on ethics of autonomous and intelligent systems. In the academic world, the MIT Media Lab and Harvard University established a $27 million initiative on ethics and governance of AI, Stanford is amid a 100-year study of AI, and Carnegie Mellon University established a centre to explore AI ethics.
Corporations are forming their own consortiums to join the conversation. The Partnership on AI to Benefit People and Society was founded by a group of AI researchers representing six of the world’s largest technology companies: Apple, Amazon, DeepMind/Google, Facebook, IBM, and Microsoft. It was established to frame best practices for AI, including constructs for fair, transparent, and accountable AI. It now has more than 80 partner companies. Foundation to fund research to accelerate fairness in AI — although some immediately questioned the potential conflict of interest of having research funded by such a giant player in the field.
Are data regulations around the corner?
There is a need to develop a global perspective on AI ethics, Different societies around the world have very different perspectives on privacy and ethics. Within Europe, for example, U.K. citizens are willing to tolerate video camera monitoring on London’s central High Street, perhaps because of IRA bombings of the past, while Germans are much more privacy oriented, influenced by the former intrusions of East German Stasi spies , in China, the public is tolerant of AI-driven applications like facial recognition and social credit scores at least in part because social order is a key tenet of Confucian moral philosophy. Microsoft’s AI ethics research project involves ethnographic analysis of different cultures, gathered through close observation of behaviours, and advice from external academics such as Erin Meyer of INSEAD. Eventually, we could foresee that there will be a collection of policies about how to use AI and related technologies. Some have already emerged, from avoiding algorithmic bias to model transparency to specific applications like predictive policing.
The longer take is that although AI standards are not top of the line sought after work, they are critical for making AI not only more useful but also safe for consumer use. Given that AI is still young but quickly being embedded into every application that impacts our lives, we could envisage an array of AI ethics guidelines by several countries for AI that are expected to lead to mid- and long-term policy recommendations on AI-related challenges and opportunities.
Chief AI ethical officer on the cards?
As businesses pour resources into designing the next generation of tools and products powered by AI, people are not inclined to assume that these companies will automatically step up to the ethical and legal responsibilities if these systems go awry.
The time when enterprises could simply ask the world to trust artificial intelligence and AI-powered products is long gone. Trust around AI requires fairness, transparency, and accountability. But even AI researchers can’t agree on a single definition of fairness: There’s always a question of who is in the affected groups and what metrics should be used to evaluate, for instance, the impact of bias within the algorithms.
Since organizations have not figured out how to stem the tide of “bad” AI, their next best step is to be a contributor to the conversation. Denying that bad AI exists or fleeing from the discussion isn’t going to make the problem go away. Identifying CXOs who are willing to join in on the dialogue and finding individuals willing to help establish standards are the actions that organizations should be thinking about today. There comes the aspect of Chief AI ethical officer to evangelize, educate, ensure that enterprises are made aware of AI ethics and are bought into it.
When done correctly, AI can offer immeasurable good. It can provide educational interventions to maximize learning in underserved communities, improve health care based on its access to our personal data, and help people do their jobs better and more efficiently. Now is not the time to hinder progress. Instead, it’s the time for enterprises to make a concerted effort to ensure that the design and deployment of AI are fair, transparent, and accountable for all stakeholders — and to be a part of shaping the coming standards and regulations that will make AI work for all
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Reimagining Strategic Management Theories And Models With Artificial Intelligence
Add Your Heading Text Here

The advent of Artificial Intelligence in the corporate world is disrupting existing business processes and changing the way organizations are run. AI is fast becoming a cornerstone of how businesses manage their bottom line, while opening new revenue streams that could provide a boost to their toplines as well. Given the scale of its impact, there is no doubt that AI will also have a severe impact on the science that governs how organizations are run today.
I am obviously referring to incumbent management theories and models that govern modern organizational management. In classic terms, management theories are frameworks of wisdom which guide the decisions made by organizational leaders that have survived phenomenally well over the period of the modern enterprise. Sure, there have been reasons to fine-tune each one to the realities of each era and industry, but the core construct has been omnipresent through the years.
With AI’s entry into the mainstream of business, management theories may need to be re-evaluated and tweaked appropriately. While the core construct remains powerfully relevant, an injection of the new-age reality of AI will help managers and business leaders apply them in a more contemporary manner on a few theories and models that are being redefined by AI.
Porter’s Five Forces
The theory of the Five Competitive Forces put forth by Michael Porter in 1979 is one of the marquee and evergreen theories in management thought schools. Michael Porter suggests that organizations looking for an understanding of their competitor environment need to consider the impact from five perspectives and work on reducing the risks associated: 1) Threat of new entrants, 2) Threat of Substitutes, 3) Bargaining Power of Customers, 4) Bargaining Power of Suppliers and 5) Intra-industry Rivalry. The construct of this theory is that when businesses need to evaluate the competitiveness (or for that matter, the probability of success) in a business or an industry, they need to keep in consideration these five levers that determine an industry’s attractiveness.
With AI now entering the fray, it is time to reimagine our understanding of Porter’s theory. Specifically, when it comes to the threat of new entrants. Over the years, AI has levelled the playing field as a secret sauce, moving even the most established incumbents from their positions in traditional industries. One must look at how AI is fuelling Amazon’s massive growth – which has hugely disrupted the traditional retail industry. Amazon uses AI in a variety of ways – from identifying the next likely purchase to piloting drone-based deliveries. It was no surprise when Amazon’s announcement last year that it will be entering the healthcare industry led to a tumble in the share price of traditional healthcare companies. AI puts enterprises in a pole position and organizations that harness its’ power correctly stand to gain huge ground over those that do not.
Elton Mayo’s Human Relations Theory
Elton Mayo’s landmark research in the field of organizational productivity comes from his studies in the 1920s at Hawthorne plants in Chicago. In seeking to answer questions around how to improve human productivity, he and his assistants tried tinkering with multiple variables that might have an impact on the quality of the labour force’s work – such as light, duration of breaks and duration of working hours. After all these variables proved inconclusive on how to uplift worker productivity, Mayo finally hit upon his hypothesis i.e. giving attention to employees is what truly resulted in improved performances. Giving your workers a voice in the decision-making process, an experience of greater freedom and autonomy and considering the inherent social needs of people – is the most critical lever in the productivity puzzle.
Enter Artificial Intelligence. With AI taking away much of the scud work involved in managing the varied bureaucracies inherent in organizations, leaders will find a lot more time in managing the performance of its most valued asset – human talent. By simplifying routine and repetitive processes for leadership and the people, we can afford to pay much more attention to the well-being of our human talent, celebrate successes and course-correct flagging performances – with the much-needed human(e) touch.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
Many models and theories surround the overall framework for TQM (Total Quality Management) – a science that owes much of its early evolution to manufacturing techniques originating in Japan. At its very essence, TQM is the science that governs the quality in the manufacturing process. It relates to the adherence of manufactured products with agreed specifications, evolved keeping in mind the needs of the end user. TQM bridges multiple concepts – from customer centricity, lowering the waste in manufacturing processes with a view to increasing the overall quality of the manufacturing output.
The theories surrounding this domain may also be due for a revamp. TQM has long been a data-driven process – relying heavily on a post-mortem understanding of evidence-based decision-making and process improvement. With AI in the picture, organizations can improve predictions around off-specified products earlier, leading to a quantum leap in manufacturing quality. AI is also helping improve the forecasting process, thus reducing the waste created through unused, unsold inventory. Similarly, AI will reduce the overhead associated with identifying anomalous manufacturing conditions and provision for predictive machine maintenance as well to keep up the quality standards in manufacturing activity.
The Future of Organizational Management
The defining case for AI to changing existing models and theories of management boils down to the need for creating a blended workforce comprising both humans and machines. Management science today is largely rooted in building more efficient and agile organizations for humans. In the future, humans and AI will work side-by-side to achieve shared organizational goals. This means that AI will help remove a lot of administrative work that often throttles the productivity of leaders – and allow them to direct their energies towards more complex, judgement driven work that requires them to think creatively. Intelligent machines will soon be considered by the workforce to be ‘colleagues’ and the evolution of management thought needs to account for policies and systems that make the most out of this hybrid workforce.
In conclusion, infusing AI will make business more human centric. Ironic as it may sound, putting AI in charge of the day-to-day, routinized activities will lead to more time for compassionate interactions between humans and unleash human creativity in a huge way. New management theories and models that emerge in the future will hence need to account for the impact of AI – and help organizations and their leaders understand how to navigate this new normal in business.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS
How AI is Challenging Management Theories and Disrupting Conventional Strategic Planning Processes
Add Your Heading Text Here

When it comes to AI, businesses think ambitiously. Nearly 85% of executives believe AI will allow their company to obtain or sustain a competitive advantage in the marketplace. Contrastingly, just one in five companies have incorporated AI into their organization and less than 39% of companies have an AI strategy.
Exactly why is AI so disruptive to traditional business models and traditional notions of industry competition? A useful way to analyse the situation is by looking at Porter’s model of the five forces of industry competition and exploring how artificial intelligence is impacting each of the various forces.
According to Michael E. Porter, in one of his landmark books, titled Competitive Strategy, “In any industry, whether it is domestic or international or produces a product or a service, the rules of competition are embodied in five competitive forces: the entry of new competitors, the threat of substitutes, the bargaining power of buyers, the bargaining power of suppliers, and the rivalry among the existing competitors.”
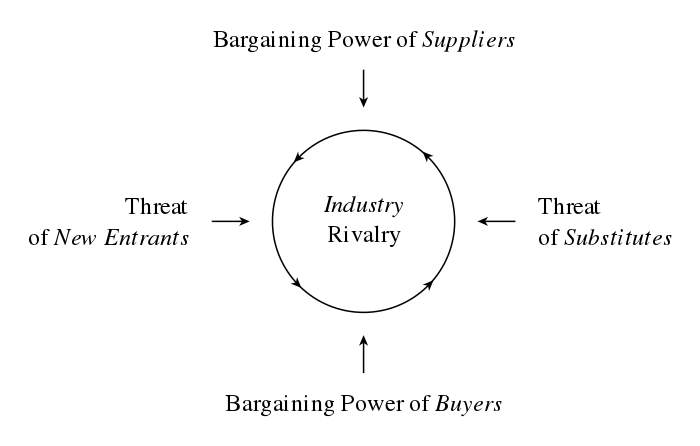
Figure 1: Porter’s Five Forces
Let’s look at each of these five forces and examine the role and impact of AI:
The entry of new competitors
There’s no doubt that AI is changing the nature of competition. Today, it’s not just traditional industry competitors you need to worry about, but new entrants from outside your industry, equipped with new AI based business models and value propositions.
This is often tech giants and startups that have envisioned and built a new business model from the ground up, powered by a new platform ecosystem for AI. They’re leveraging the familiar social, mobile, analytics and cloud technologies, but are often adding in personas and context, intelligent automation, chatbots and the Internet of Things, to further enhance the value proposition of their platform.
Why can new entrants move in so easily? Digital business changes the rules by lowering the traditional barriers to entry. A digitally based business model requires far less capital and can bring large economies of scale for example. Read more about how AI Startups are creating disruptive competition here.
The threat of substitutes
The threat of substitutes is high in many industries since switching costs are low and buyer propensity to substitute is high. For example, In the taxi services, customers can easily switch from traditional models to the new digital app based taxi services, employing AI routines to create differential pricing and intelligent route mapping to increase margin as well as decrease price for the customers. Propensity to switch from the traditional model is high due to consumer wait times for taxis, lack of visibility into taxi location and so on.
In case of BPO industry, the advent of AI has been extremely disruptive, with their clients completely substituting their services with building in-house automation offerings and circumventing their need, sometimes completely. Read more in detail about the disruption of BPO/BPM by AI here.
The bargaining power of buyers
Perhaps the strongest of the five forces impacting industry competition is the bargaining power of buyers since the biggest driver of AI and digital business comes from the needs and expectations of consumers and customers themselves.
This bargaining power lays out a new set of expectations for the AI and digital customer experience and necessitates continual corporate innovation across business models, processes, operations, products and services.
For example, the most used instances of chatbots are through customer support, and now they are heading in the direction of changing the retail sector altogether. The expectations of the Millennials are directing the course of this new technology. This is why chatbots have the burden to exceed the expectations in the retail sector.
Also, in another example, in the customer facing marketing aspect, AI is causing circular rise in customer expectations as rise of expectations, mostly from millennials, has forced the companies to adopt an AI solution to the problem, which further has emboldened their expectations. Amazon, the company that wants to eat everyone’s lunch, is already driving a third of its business from a AI-powered function: its recommended purchases. Read more about how AI is accentuating customer experience to address rising expectations Here.
The bargaining power of suppliers
Suppliers can accelerate or slow down the adoption of a AI based business model based upon how it impacts their own situation. Those pursuing AI models themselves, such as the use of APIs to streamline their ability to form new partnerships and manage existing ones, may help accelerate your own model.
Those who are suppliers to the traditional models, and who question or are still determining their new role in the digital equivalent, may use their bargaining power to slow down or dispute the validity or legality of the new model.
Good examples are the legal and business issues surfacing around the digital-sharing economy (i.e. ride-sharing, room-sharing etc.) where suppliers and other constituents work to ensure the AI based business model and process innovations (like route optimization, or deep customer behaviour analysis using private data) still adhere to established rules, regulations, privacy, security and safety. This is a positive and needed development since, coupled with bargaining power of buyers, it can help to keep new models “honest” in terms of how they operate.
The rivalry among the existing competitors
A lot of organisations are in exploratory stages as they realise that their strategy and customer engagement needs to get smarter. The combination of optimism and fear that clients today have shows that for them it is a competitive necessity to adopt AI and digital technologies.
In 20 years, probably every job will be touched by AI. The technology is growing universally. WhatsApp and Facebook — everything is driven by AI. And what this means is that on the job front, there may be blood. Once AI, ML, and virtual and augmented reality go mainstream, these technologies will prove to be a huge job creator.
But currently, the most competitive space in AI adoption is in the implementation of chatbots across industries and functions. While we might see chatbots starting to appear through the likes of Facebook Messenger and WhatsApp platforms in the coming 12 months, and will be dedicating teams of engineers to train the platforms, rather than relying on the general public. Read more about the competitive atmosphere and underlying need to better customer experience using chatbot here.
How AI will transform Strategic Planning Process
How can managers — from the front lines to the C-suite — thrive in the age of AI? In many ways, the lack of understanding when it comes to AI is due to the variety of ways AI can be implemented as a part of strategic planning for a business. Different industries, or even different companies within the same industry, may use AI in different ways. Ping An, which employs 110 data scientists, has launched about 30 CEO-sponsored AI initiatives that support, in part, its vision – that technology will be the key driver to deliver top-line growth for the company in the years to come. Yet in sharp contrast, elsewhere in the insurance industry, other large companies’ AI initiatives are limited to experimenting with chatbots. Obviously, integrating AI is not going to be simple. There will be a massive learning curve for organizations before they’re able to start implementing AI effectively. But the core shift in strategic planning will happen in the following ways:
AI will take over almost all Administrative Tasks
According to an HBR report, managers across all levels spend more than half of their time on administrative coordination and control tasks. (For instance, a typical store manager or a lead nurse at a nursing home must constantly juggle shift schedules because of staff members’ illnesses, vacations, or sudden departures.) These are the very responsibilities that the same managers expect to see AI affecting the most. And they are correct: AI will automate many of these tasks.

Figure 2: Source – HBR (How Artificial Intelligence Will Redefine Management)
For example, in case of report writing The Associated Press expanded its quarterly earnings reporting from approximately 300 stories to 4,400 with the help of AI-powered software robots. In doing so, technology freed up journalists to conduct more investigative and interpretive reporting.
Strategy Managers will focus more on Judgement-oriented Creative Thinking Work
The human factor, which AI still cannot permeate – the application of experience, expertise and a capacity to improvise, to critical business decisions and practices – need to be focused on by strategy managers. Many decisions require insight beyond what artificial intelligence can squeeze from data alone. Managers use their knowledge of organizational history and culture, as well as empathy and ethical reflection. Managers we surveyed have a sense of a shift in this direction and identify the creative thinking skills and experimentation, data analysis and interpretation, and strategy development as three of the four top new skills that will be required to succeed in the future. And since the potential of machine learning is the ability to help make decisions, the AI technology would be better placed as an assisting hand than administrative mind.
Think of AI not as Machines, but Colleagues
Managers who view AI as a kind of colleague will recognize that there’s no need to “race against a machine.” While human judgment is unlikely to be automated, intelligent machines can add enormously to this type of work, assisting in decision support and data-driven simulations as well as search and discovery activities. In fact, 78% of the surveyed managers believe that they will trust the advice of intelligent systems in making business decisions in the future.
Not only will AI augment managers’ work, but it will also enable managers to interact with intelligent machines in collegial ways, through conversation or other intuitive interfaces.
For example, Kensho Technologies, a provider of next-generation investment analytics, allows investment managers to ask investment-related questions in plain English, such as, “What sectors and industries perform best three months before and after a rate hike?” and get answers within minutes.
Design Thinking needs to be adopted both ways – Managers & AI
While managers’ own creative abilities are vital, perhaps even more important is their ability to harness others’ creativity. Manager-designers bring together diverse ideas into integrated, workable, and appealing solutions. Creative thinking and experimentation is a key skill area that managers need to learn to stay successful as AI increasingly takes over administrative work. ‘Collaborative Creativity’ is the operating word here.
But this doesn’t mean that design thinking necessarily need to become a forte exclusive to managers. Even though AI engines may not have reached radical thinking and improvisation as humans, AI algorithms should be viewed as cognitive tools capable of augmenting human capabilities and integrated into systems designed to go with the grain of human—and organizational—psychology. This calls for Divergence from More Powerful Intelligence To More Creative Intelligence in AI.
To make design thinking meaningful for consumers, companies can benefit from carefully selecting use cases and the information they feed into AI technologies. In determining which available data is likely to generate desired results, enterprises can start by focusing on their individual problems and business cases, create cognitive centres of excellence, adopt common platforms to digest and analyze data, enforce strong data governance practices, and crowdsource ideas from employees and customers alike. Read more about Design Thinking in AI here.
Create New Business Processes manifested from Augmented Working Strategy
Simply put, my recommendation is to adopt AI in order to automate administration and to augment but not replace human judgment. If the current shortage of analytical talent is any indication, organizations can ill afford to wait and see whether their managers are equipped to work alongside AI. This calls for change in business processes, and the way they are implemented itself. To navigate in an uncertain future, managers must explore early, and experiment with AI and apply their insights to the next cycle of experiments.
AI augmentation will drive the adoption of new key performance indicators. AI will bring new criteria for success: collaboration capabilities, information sharing, experimentation, learning and decision-making effectiveness, and the ability to reach beyond the organization for insights.
Accordingly, organizations need to develop training and recruitment strategies for creativity, collaboration, empathy, and judgment skills. Leaders should develop a diverse workforce and team of managers that balance experience with creative and social intelligence — each side complementing the other to support sound collective judgment.
Final Word
While oncoming AI disruptions in Management Principles and Strategic Planning space won’t arrive all at once, the pace of development is faster and the implications more far-reaching than most executives and managers realize. Those managers capable of assessing what the workforce of the future will look like can prepare themselves for the arrival of AI.

