
Future of Work 2020: Sameer Dhanrajani, Co-founder of AIQRATE, shares his take on the power of AI
Add Your Heading Text Here

Will artificial intelligence (AI) take over human intelligence? Is AI applicable across every industry? What is the cost of implementing AI, is it expensive? Is AI complex? AI is not for the masses?
There is hardly any industrial domain today which is not harnessing the benefits of artificial intelligence to accomplish efficiency, accuracy, and affordability, while cutting down on the time taken by manual processes. And yet, there are a million myths surrounding this re-merging tech tool that continues to question the utility and implementation of AI in day-to-day activities.
Sameer Dhanrajani, Chief Executive Officer and Co-founder, AIQRATE Advisory & Consulting, busted some of these myths on Day 1 of Future of Work, India’s largest product-tech-design conference hosted by YourStory.
To explain his point further, he cited the example of Japan’s Makoto Koike. An engineer by education, Makoto went back to his parent’s cucumber farm and began developing a new approach with the help of technology. In the process, Makoto realised there was something in the making – the making of an algorithm, which could give him some understanding about the yield, crop, and the prices. And this is just one area of the application of AI.
According to Sameer, there are at least three strategic imperatives for growth through AI and it involves re-imagining customer experiences, innovating new products and services, and transforming businesses. The AI advisor also touched upon the algorithm economy, explaining how algorithms are impacting modern decision making.
From healthcare to education, sanitation, and marketing practices, artificial intelligence is making its presence felt across sectors today. While AI alone might not be able to address all issues and solve all the problems, Sameer notes that combined with data intelligence and design, it can surely revolutionise the future.
Read more at: https://yourstory.com/2020/02/future-of-work-sameer-dhanrajani-artificial-intelligence
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

Experience the Algorithm Economy : Accentuating strategic value for the enterprises
Add Your Heading Text Here

Algorithms will not only drive scores of business processes, but also build other self-intuitive algorithms, much as robots can build other robots. And rather than using apps, future users’ lives will revolve personalized algorithms to drive individual choices and behaviors .
Enterprises will license, trade, sell and even give away non-lynch pin algorithms and single-function software snippets that provide new opportunities for innovation by other enterprises. Enterprises will also partner with cloud-based, automated suppliers with the industry expertise to advice on ways to avoid future risk and adapt to technology trends.
Imaginative thinking ! but it’s no surprise that future value will come from increased density of interactions, relationships and sharing between people, businesses and things ̶ or what I call “ Algorithm Economy “ .The greater the maturity of algorithms , the greater potential value you can reap. We’ve seen interconnection coming of age for a while now and have invested heavily in a platform to empower enterprises with fast, direct and secure interconnections with business partners and network and cloud service providers.
Redefining Business Architecture with Algorithms
The term “algorithm economy” is relatively new, but the practical use of algorithms is already well established in many industries. In my opinion , CXOs must begin designing their algorithmic business models, both to capitalize on their potential for business differentiation, and to mitigate the possible risks involved.
Established businesses need to adopt a “bi modal strategy” and build what I called an algorithmic platform, completely separate from legacy systems, that harnesses repository of algorithms, interconnections, the cloud and the Internet of Things (IoT) to innovate, share value, increase revenues and manage risk.
New platforms based on this bimodal model should be far simpler, more cloud-based and more flexible than in the past, with the ability to add and remove capabilities “like Velcro” to support new short- and long-term projects. At the same time, IT should start divesting itself of older systems and functions that are outliving their usefulness or could be better done by other methods. The significant development and growth of smart machines is a major factor in the way algorithms have emerged from the shadows, and become more easily accessible to every organization. We can already see their impact in today’s world, but there is much work ahead to harness the opportunities and manage the challenges of algorithmic business.
CXOs should examine how algorithms and intelligent machines are already used by competitors and even other enterprises to determine if there is relevance to their own needs. The retail sector has long been at the leading edge of using smart algorithms to improve business outcomes. Today, many retail analysts believe that the algorithms that automate pricing and merchandising may soon become the most valuable asset that a retailer can possess. In HR function, algorithms are already transforming talent acquisition as they are able to rapidly evaluate the suitability of candidates for specific roles, but the same technology could easily be applied within an enterprise to allocate workloads to the right talent. In healthcare, the open availability of advanced clinical algorithms is transforming the efficiency of healthcare delivery organizations and their ability to deliver care. The practice of sharing and co-developing algorithms between enterprises with mutual interests could be relevant to most enterprises.
The Challenges of Algorithm Economy
The advances and benefits of algorithm economy will come hand in hand with obstacles to navigate. Whether the problems are anticipated or unexpected, as quantum computing becomes more pervasive, the implications have the potential to make or break organizations. For example, an extreme point of view is that any beneficial effects of algorithms on humanity may be nullified by algorithmically driven systems that are antithetical to human interests. Or, while an algorithmic business model may be deployed with good intentions, it could be manipulated by malicious humans to achieve undesirable outcomes. Undesirable, at least, from the point of the view of the person or organization that owns or controls the algorithm. Algorithms rely on the data they are fed, and their decisions are only as good as the data they are based on. Moreover, tricky ethical problems that do not necessarily have a “correct” answer will be inevitable, as a greater complexity of decision making is left in the hands of automated systems.
The scale of change that is made possible by smart machines and algorithm economy warrants considerable planning and testing. Enterprises that fail to prepare risk being left behind or facing unexpected outcomes with negative implications.
The Transformation required in Algorithm Economy
Making sense of all the data about how customers behave, and what connected things tell an organization, will require algorithms to define business processes and create a differentiated customer experience. Algorithms will evaluate suppliers, define how our cars operate, and even determine the right mix of drugs for a patient. In the purely digital world, agents will act independently based on our algorithms, in the cloud. In the 2020s, we’ll move away from using apps to rely on virtual assistants – basically, algorithms in the cloud – to guide us through our daily tasks. People will trust personal algorithms that thinks and acts for them. Take this to another level and the algorithms themselves will eventually become smart by learning from experience and producing results their creators never expected.
The Final Frontier
Therefore, we have to get the architecture of algorithms robust and steady to derive meaningful objectives. In essence, algorithms spot the business moments, meaningful connections, and predict ill behaviors and threats. CXOs need to be the strategic voice on the use of information, to build the right set of intelligent insights. Experience the Algorithm Economy and the ensuing strategic value for your enterprise . Are you geared up ?
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

How AI is shaping the new life in life sciences and pharmaceutical industry
Add Your Heading Text Here

The pharma and life sciences industry is faced with increasing regulatory oversight, decreasing R&D productivity, challenges to growth and profitability, and the impact of artificial intelligence (AI) in the value chain. The regulatory changes led by the far-reaching Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) in the US are forcing the pharma and life sciences industry to change its status quo.
Besides the increasing cost of regulatory compliance, the industry is facing rising R&D costs, even though the health outcomes are deteriorating and new epidemics are emerging. Led by the regulatory changes, the customer demographics are also changing. The growth is being driven by emerging geographies of APAC and Latin American region.
Disruption in life sciences
Pharmaceutical organisations can leverage AI in a big way to drive insightful decisions on all aspects of their business, from product planning, design to manufacturing and clinical trials to enhance collaboration in the ecosystem, information sharing, process efficiency, cost optimisation, and to drive competitive advantage.
AI enables data mining, engineering, and real time- and algorithmic-driven decision-making solutions, which help in responding to the following key business value chain disruptions in the pharmaceutical industry:
- AI-driven drug discovery – Enables scientists to source scientific findings and insights from external labs or internal knowledge to jump start discovery which will in turn help reduce cycle time for product development aiding faster go-to-market
- Reduce cycle times for clinical trials– Through better insights driven by improved accuracy of machine-based ensemble algorithms
- Supply chain transformation – Building predictive algorithms using a combination of internal and external data would help reduce unforeseen shortages in availability of drugs impacting customer service levels and lost sales revenues
- Product failure prediction – Via root cause analysis and predictive algorithms of product failures (vendor data)
- Risk management – For evaluation of potential risks posed by elemental impurities in a formulated drug product
- Real-time medical device analysis and visualisation– Leveraging interconnecting data from implanted devices and personal care devices
- Behavioural sciences – To more fully understand customer perceptions about their products which helps in proactively fixing product issues or managing communication better
- Enhance reporting systems– To meet the changing regulatory compliance needs more effectively
- Intelligent insights – Renew focus on understanding the underlying business data and generating insights using latest insights and intelligence frameworks
The human microbiome
Though genomics currently hogs the spotlight, there are plenty of other biotechnology fields wrestling with AI. In fact, when it comes to human microbes – the bacteria, fungi, and viruses that live on or inside us – we are talking about astronomical amounts of data. Scientists with the NIH’s Human Microbiome Project have counted more than 100 trillion microbes in the human body.
- Cambridge Semantics has a developed semantic web technologies that help pharmaceutical companies sort and select which businesses to acquire and which drug compounds to license.
- Data scientists at the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard have developed the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV), open source software that allows for the interactive exploration of large, integrated genomic datasets.
- GNS Healthcare is using proprietary causal Bayesian network modeling and simulation software to analyse diverse sets of data and create predictive models and biomarker signatures.
Genomics
- Sequencing millions of human genomes would add up to hundreds of petabytes of data.
- Analysis of gene interactions multiplies this data even further.
In addition to sequencing, massive amounts of information on structure/function annotations, disease correlations, population variations – the list goes on – are being entered into databanks. Software companies are furiously developing tools and products to analyse this treasure trove.
Robust algorithms with massive data engineering capabilities
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

How the insurance industry can leverage AI to enhance efficiencies
Add Your Heading Text Here

This second machine age has seen the rise of artificial intelligence (AI), or intelligence that is not the result of human cogitation. AI is now ubiquitous in many commercial products, from search engines to virtual assistants.
The massive amounts and the speed at which structured and unstructured (e.g., text, audio, video, sensor) data is being generated has made speedy processing and generation of meaningful, actionable insights imperative.
The insurance industry segment has been conservative in adopting AI across the value chain, but P&C /Life/Reinsurance companies have accelerated the pace of AI adoption and initiated deployment of AI use cases across the value chain.
Here are few of the use cases leveraging AI for the insurance industry:
Personalised customer experience: redefining the value proposition
Many insurers are already in the early stages of enhancing and personalising the customer experience. Exploiting social data to understand customer needs and sentiments about products and processes (e.g., claims) are some early applications of AI.
The next stage in robo-advisor evolution is to offer better intelligence on customer needs and goal-based planning for both protection and financial products. Recommender systems and “someone like you” statistical matching will become increasingly available to customers and advisors.
Up next will be understanding of individual and household balance sheets and income statements, as well as economic, market, and individual scenarios to recommend, monitor and alter financial goals and portfolios for customers and advisors.
Automated and augmented underwriting: enhancing efficiencies
This involves automating large classes of standardised underwriting in auto, home, commercial (small and medium business), life, and group using sensor (IoT) data, unstructured text data (e.g., agent/advisor or physician notes), call centre voice data, and image data using Bayesian learning or deep learning techniques.
The industry will also model new business and underwriting process using soft robotics and simulation modeling to understand risk drivers and expand the classes of automated and augmented (i.e., human-performed) underwriting.
We will also see augmenting of large commercial underwriting and life/disability underwriting by having AI systems (based on NLP and DeepQA) highlight key considerations for human decision-makers. Personalised underwriting by a company or individual takes into account unique behaviours and circumstances.
Robo-claims adjuster
This will help build predictive models for expense management, high value losses, reserving, settlement, litigation, and fraudulent claims using existing historical data. It will also help analyse claims process flows to identify bottlenecks and streamline flow, leading to higher company and customer satisfaction.
Building a robo-claims adjuster by leveraging predictive models and building deep learning models that can analyze images to estimate repair costs can change status quo. In addition, use of sensors and IoT to proactively monitor and prevent events can reduce losses.
A claims insights platform that can accurately model and update frequency and severity of losses over different economic and insurance cycles (i.e., soft vs. hard markets) can help the industry. Carriers can apply claims insights to product design, distribution, and marketing to improve overall lifetime profitability of customers.
Emerging risks and new product innovation
Identifying emerging risks (e.g., cyber, climate, nanotechnology), analyse observable trends, determining if there is an appropriate insurance market for these risks, and developing new coverage products in response historically have been creative human endeavors.
Man and machine learning
Artificial general intelligence (AGI) that can perform any task that a human can is still a long way off. In the meantime, combining human creativity with mechanical analysis and synthesis of large volumes of data – in other words, man-machine learning (MML) – can yield immediate results.
For example, in MML, the machine learning component sifts through daily news from a variety of sources to identify trends and potentially significant signals. The human learning component provides reinforcement and feedback to the ML component, which then refines its sources and weights to offer broader and deeper content.
Using this type of MML, risk experts (also using ML) can identify emerging risks and monitor their significance and growth. MML can further help insurers to identify potential customers, understand key features, tailor offers, and incorporate feedback to refine new product introduction.
AI implications for insurers
Improving Efficiencies: AI is already improving efficiencies in customer interaction and conversion ratios, reducing quote-to-bind and FNOL-to-claim resolution times, and increasing new product speed-to market. These efficiencies are the result of AI techniques speeding up decision-making (e.g., automating underwriting, auto-adjudicating claims, automating financial advice, etc.).
Improving effectiveness: Because of the increasing sophistication of its decision-making capabilities, AI soon will improve target prospects to convert them to customers, refine risk assessment and risk-based pricing, enhance claims adjustment, and more. Over time, as AI systems learn from their interactions with the environment and with their human masters, they are likely to become more effective than humans and replace them. Advisors, underwriters, call centre representatives, and claims adjusters likely will be most at risk.
Improving risk selection and assessment: AI’s most profound impact could well result from its ability to identify trends and emerging risks, and assess risks for individuals, corporations, and lines of business. Its ability to help carriers develop new sources of revenue from risk and non-risk based information will also be significant.
Read more at: https://yourstory.com/2020/02/insurance-industry-leverage-ai-enhance-efficiencies
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

AI for Startups: 4 adoption recommendations entrepreneurs should keep in mind
Add Your Heading Text Here

Despite nationwide venture funding hitting a multiyear low, venture capital deployed to artificial intelligence (AI) startups has reached a record high.
Last year, VCs struck 859 deals with AI companies, nearly five times the number that signed on the dotted line four years earlier. To date, the market has 2,045 AI startups and more than 17,000 market followers, with more joining by the day.
AI’s rapid rise has swept up startups and enterprises alike, including US automaker Ford, which recently bought AI startup Argo for $1 billion. The acquisition cements experts’ suspicions of Ford’s coming foray into self-driving technology. Other startups — so many, in fact, that entrepreneurs need a “best of” guide — are betting heavily on bot platforms.
Sixty-eight percent of marketing executives report using AI in their function. For a practice that only went mainstream in 2016 and barely existed four years ago, that’s a remarkable adoption rate.
How, regardless of the platform you choose, can you join forward-thinking entrepreneurs and build your business with AI? Over the last few years, I have worked closely with multiple startups across genres and ,So far, four strategic considerations stand out to leverage AI in your startups:
1. Get to know your next customer
A politician wouldn’t dream of delivering a small-town stump speech to urban constituents. Why? Because you’ve got to know your audience. The same is true for entrepreneurs. Before you broadcast your message, you need to know who you’re trying to reach.
Node, an account-based intelligence startup, uses natural language processing — a fancy term for teaching a computer to understand how we humans speak and write — to develop customer profiles. Node is crunching vast swaths of data to connect the dots between marketers and companies they’re trying to reach.
Once you have ample customer data — Node uses data crawlers to scrape information from social media, news sites, and more — pair machine learning and natural language processing models to extract sentiments from unstructured data. Then, just as senators segment constituents into demographic groups, Node uses cluster analysis to sort clients’ customers into like cohorts.
2. See how people truly use your product
If, heaven forbid, you forgot to tag your neighbour at last week’s house party, Facebook was no doubt there to remind you of your error. How does Facebook know which of your friends you left untagged? It has gone all-in on an AI technique called convolutional neural networks.
Convolutional neural networks, which loosely model how the brain’s visual cortex interacts with the eyes, work by separating an image into tiny portions before running each of those specks through a multilayered filter. It then “sees” where each speck overlaps with other parts of the image, and through automated iterations, puts together a full image.
Many different ways exist to apply this technology, but retail businesses can start with image classification. Try using a convolutional neural network to break down photos of your products posted online. The model can identify customer segments that frequently use your product, where they’re using it and whether they commonly pair other products with yours. Essentially, this automated image analysis can show you how your products fit into customers’ lives, allowing you to tailor your marketing materials to fit.
3. Get inside the user’s experience
Fortunately, AI can take the emotional temperature of thousands of customers at once. Dumbstruck, a video-testing and analytics startup that I advise, has added natural language processing to its emotional analytics stack. This allows it to provide moment-by-moment insights into viewers’ reactions to media. Dumbstruck’s model grows stronger with each reaction analysed, producing a program that perceives human emotions even better than some people can.
4. Provide affordable, always-on support
Customer service is — or should be, according to consumers — the department that never sleeps. More than half of people, 50.6 percent to be precise, believe a business should be available 24/7 to answer their every question and concern. When asked whether businesses should be available via a messaging app, the “yes” votes jump to nearly two in three. Fortunately, bots don’t sleep, eat or go off-script.
A well-built bot can offer cost-effective, constant customer service. Of course, grooming your bot to serve customers requires front-end data — ideally hundreds of thousands of example conversations — but you can get started with a human-chatbot hybrid. With this approach, the bot answers run-of-the-mill questions, while a human takes over for the more complex ones. Then, as data builds and the model matures, you can phase in full automation.
AI’s impact on startups
Startups will gain a competitive edge in capturing the AI market. Larger enterprises will provide the infrastructure to startups for building innovative services. It is somewhat similar to the business model followed when cable technology was introduced.
Startups leveraging AI technology for industry verticals, including agriculture, manufacturing or insurance, are bound to be successful.
Startups can empower established insurance companies like State Farm, Allstate, and Farmers with technology, enabling them to become more proactive in policy planning. For instance, a new AI insurance underwriter will help to forecast natural disasters and accidents, and adjust premiums.
The predictive, decision-making capabilities are more than just a novel technology. You can manage food supply chains with the help of AI. Startups could develop end-to-end farming solutions with AI analytics for reducing food waste. It will have a huge impact in tackling global issues of hunger and famine.
AI will be a fundamental predictive enabler helping us solve large-scale problems, and startups are poised to gain a competitive edge.
Ground-level AI sentiment of startups Regardless of which industry you operate, AI will affect your world in some way. Look into what is present now and how you can use it to gain a competitive edge. The possibilities with AI are endless; enterprises will become efficient, intelligent, and cost-effective. Undoubtedly, the AI revolution will advance to a point where it will offer real-world benefits to every business, large and small.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

AIQRATE is the Official Partner for Future of Work 2020
Add Your Heading Text Here

AIQRATE is the official partner for the India’s largest product-tech-design conference “Future of Work 2020” scheduled on Feb 28 and 29 in Bengaluru.
Some of India’s most successful Founders, CXOs, Data Science and Design Heads, would be present here to discuss their vision for the future of business and what they’re doing with tech, analytics & design to lead the change.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS

AI to be $100 billion sector by 2025
Add Your Heading Text Here

- Agriculture – AI holds the key to unlock massive value from India’s agrarian economy by leveraging data to better predict and improve farm yield, speeding up agricultural finance, crop insurance, Kisan help centres and helping predict demand for agricultural produce. I.e. AI sensors in ponds help farmers to gain maximum value from shrimp farming through predictive maintenance.
- Smart Cities – Al driven interventions can add substantial value in analyzing local intelligence to improve traffic conditions and providing predictive intelligence on infrastructure development. It can be used to decentralised and decongest major cities and play a key role in predictive maintenance activities.
- Skilling – Utilizing AI to predict demand for skills and equip educational institutions with insights to train the future workforce.
- Swachh Bharat – Al and specifically computer vision can help substantially improve the success of Swachh Bharat. Al is already being used in the campaign in a big way. There is a WhatsApp number outside every sanitation facility. The user can send photographs of unhygienic conditions without providing any details. The photo will be processed at a central command centre and a call will be made to the vendor within 45 seconds to fix the facility. This is all being done at a cost of Rs 2 crores a month only.
- Healthcare – India’s high and diverse population makes it fertile ground for population health studies. Al can be employed to provide evidence-based treatment options and analyzing clinical notes to suggest a treatment procedure.
- Governance – AI can power several governance initiatives ranging from security threats, RTI, potential fraud and corruption to improving the legal system, curbing human trafficking and tracking of missing persons.
Qualitas Technologies has been recognized as the Best Start up for Innovative deployment of Industrial AI in large scale corporate environment.
The summit witnessed a live audience poll for the presentation made by the Start-ups and Orbo.ai was recognized has Best Start up (Audience poll category).
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS
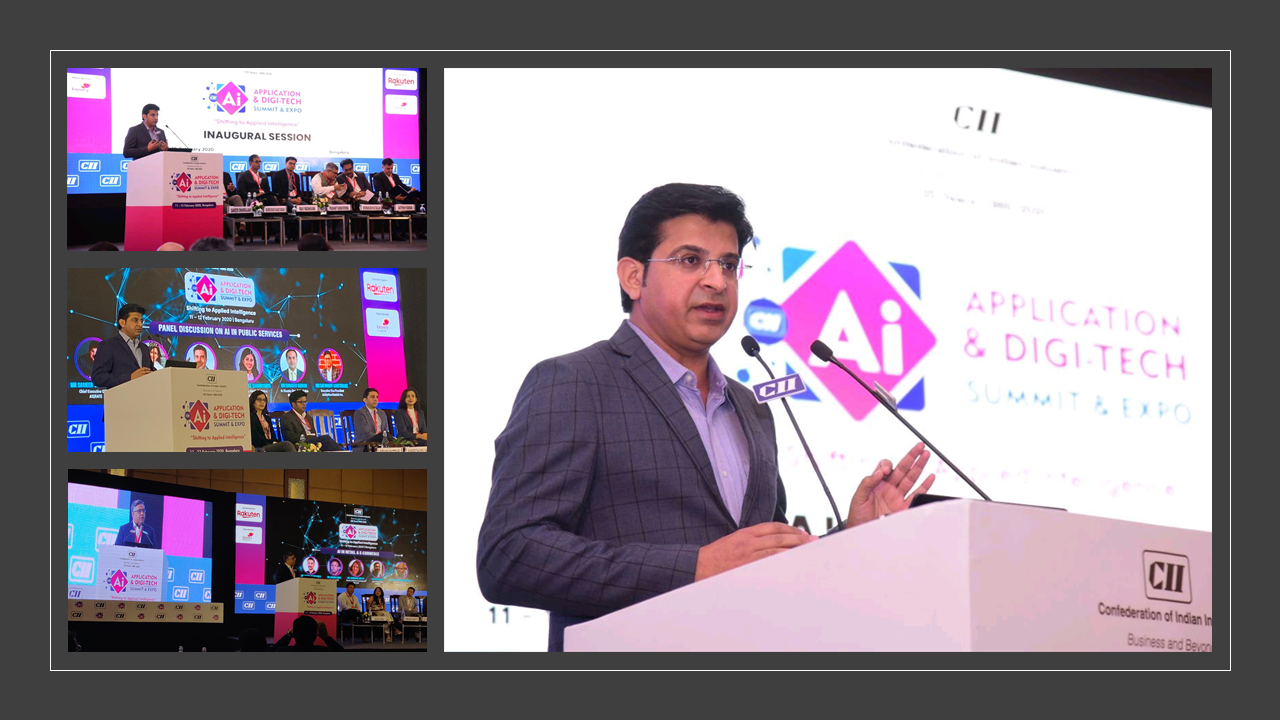

AIQRATE at AI Summit & Expo 2020 Organized by CII
Add Your Heading Text Here

AIQRATE was at the engaging and engrossing AI Summit & Expo organized by CII (Confederation of Indian Industry) on 11-12 February 2020 in Bengaluru. “AI Applications & Digi-Tech” being the main theme transcends wide array of applications and adoptions by multiple industry segments leveraging AI.
Keynote session by Sameer Dhanrajani, CEO at AIQRATE, focused on AI becoming new normal in business transformation and driving strategic imperatives in the enterprises.
Sameer also moderated an interesting panel discussion on “AI in Public Services“. In this discussion, panelists touched upon several applications of AI across public services domains including governance, utilities, education and legal.
In a separate session on “AI in Retail & e-Commerce”, Rohan Nag, Chief Client Officer at AIQRATE, explained multiple disruptive implementations of AI enabled solutions in retail domain.
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS
How AI is powering the Future of Work: key considerations for business and tech leaders
Add Your Heading Text Here

The age of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is upon us. Businesses and society are now looking towards AI for transformative outcomes. Businesses, specifically, are investing huge amounts of money on AI that will not only bring in efficiencies across multiple processes, but also unlock new revenue streams that will deliver significant top line and bottom-line impact. With the AI transformation playing out rapidly in our personal and professional lives, we need to deeply understand what the future of work will look like in the age of AI.
Business executives are now needed to deeply understand the potential of AI and translate it into a viable roadmap for their business. Technology leaders need to take centre-stage in how their organisations adopt and harness the power of AI. We are seeing a fast proliferation of digital evangelists and transformation officers who are charged with developing a framework within which the future of the organisation will operate.
Future of Work, redefined
On a tactical level, the burning question now is: how can organisations build a steady pipeline of future talents with expertise in AI? Mastery of exponential technologies (AI, cloud computing, blockchain, IoT, cybersecurity, etc) will be remarkably important for both business and technical professionals.
For us to redefine the future of work powered by AI, we need to ensure that a few key enablers come together. We need to expand the scope of executive education and the courseware that goes with it. Next, we need to seriously consider the potential impact of crisp yet impactful courses. Corporations need to augment their training programmes with shorter, time-boxed courseware that can deliver instant impact for the organisation.
Finally, we need to reimagine multiple, personalised career pathways. We need to move away from the traditional one-size-fits-all training and deliver more tailored, fit-for-purpose and relevant education to employees.
Here are the three critical interventions for the business and technology leaders to execute in order to usher in the future of work that is enabled by AI.
Develop new-age skills and competencies in AI
Upgrading the technology competencies and skills of business and technology leaders and their teams seems like the most critical first step. With the landscape of technology is rapidly evolving, we need to urgently upskill the present and future workforce to ensure a quality supply of talent.
On a broader scale, we also need universities and colleges to improve the existing knowledge base of AI-enabling technologies such as cloud, DevOps, blockchain, etc, as well for the workforce.
At present, we see a decent level of advancement in the field of computer science training and education. However, other trades within the technical area also require to be upgraded as well. By doing so, we will be able to ensure wholesome and future-proof education for aspirants who wish to build their careers in the world of AI.
For instance, those studying for a major in the field of electronics could shape their focus on mastering AI-enabling technologies such as GPUs and quantum computing. The students presently pursuing a specialisation in mechanical engineering could achieve some level of sophistication in allied subjects of robotics and 3D printing.
Subject matter experts in the fields of industrial engineering, operations, and supply chain would also do well to extend their skill sets to ML and blockchain as well, thus creating a convergence of their interest areas and realities of the market, which will empower them with the required tools to succeed in the workplace of the future.
Read this on YourStory.com: https://yourstory.com/2020/02/ai-transformation-future-work-business-tech-leaders
Related Posts
AIQRATIONS
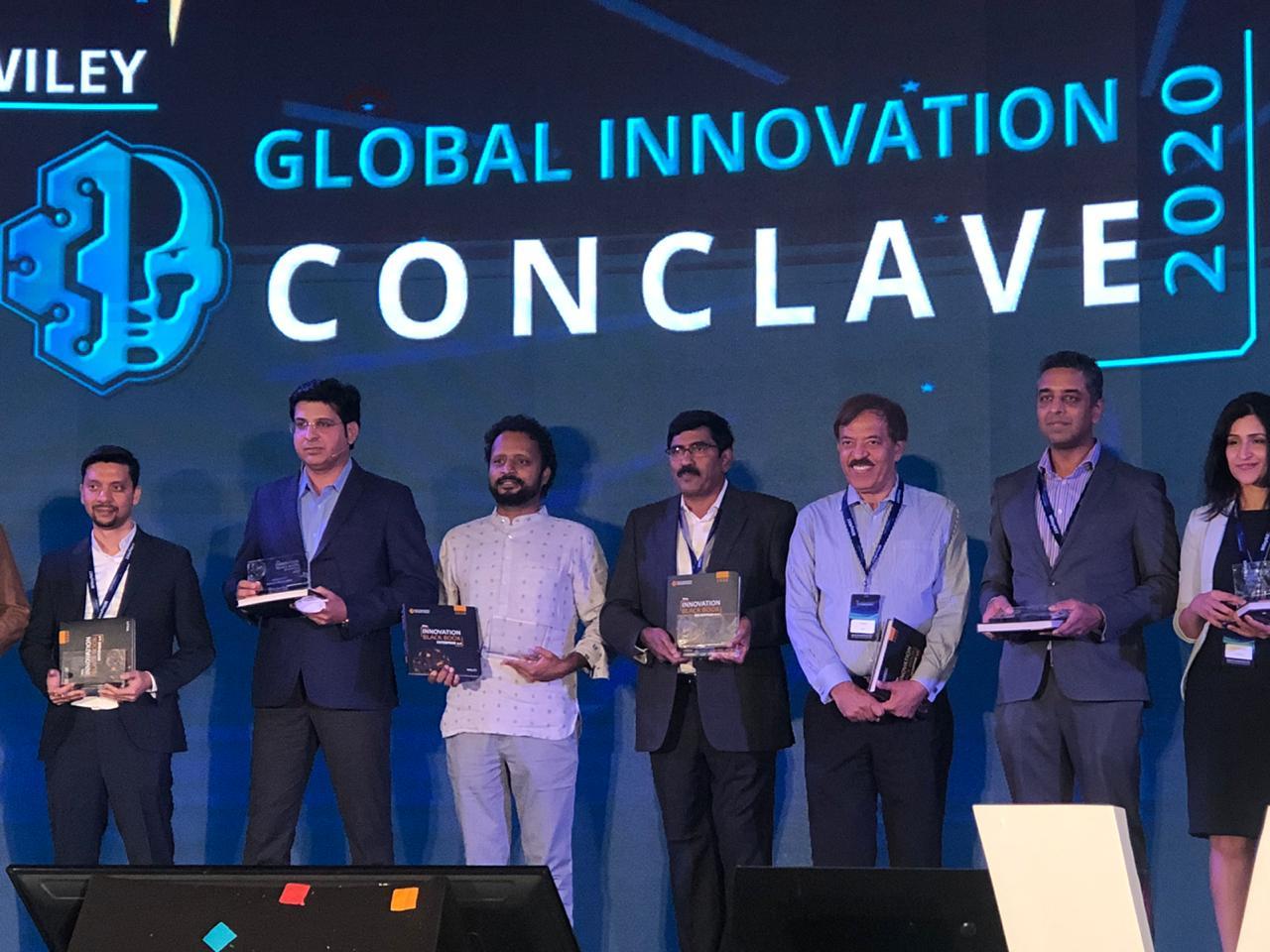

AIQRATE at the launch of Wiley Innovation Black Book 2020 in Wiley Innovation Conclave
Add Your Heading Text Here

A confluence of 24 industry leaders and academic heads converged yesterday at Wiley innovation conclave to launch Wiley innovation Black Book 2020. The book is a marquee compilation of future forward perspectives of top leaders, as they envision how the enterprises of the future will operate the business and customer models, functional value chains as well as various digital assets and enablers. It also dwells on increasing significance of GCCs in the ecosystem. Sameer Dhanrajani, CEO at AIQRATE Advisory & Consulting was the Series Editor of the black book 2020 working along with Vikas Gupta, MD at Wiley India and Debabrati Sengupta, GM at Wiley India.
Click here for Wiley Innovation Black Book 2020 – Enterprise 4.0.


